

| Reference: | CO-516 |
| Author | Athanasius KIRCHER |
| Year: | 1671 |
| Zone: | Tivoli |
| Printed: | Amsterdam |
| Measures: | 410 x 340 mm |


| Reference: | CO-516 |
| Author | Athanasius KIRCHER |
| Year: | 1671 |
| Zone: | Tivoli |
| Printed: | Amsterdam |
| Measures: | 410 x 340 mm |
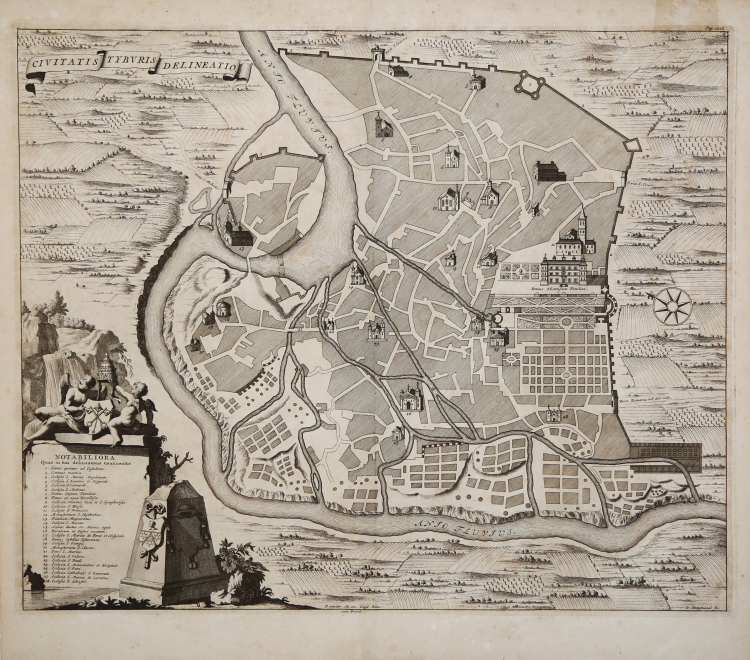
Map of Tivoli taken from the LATIUM. ID EST NOVA & PARALLELA LATII TUM VETERIS TUM NOVI DESCRIPTIO printed in Amstelodami: Apud Joannem Janssonium À Waesberge, & Haeredes Elizei Weyerstraet, 1671.
Latium is a 1669 work by the Jesuit scholar Athanasius Kircher. It was dedicated to Pope Clement X and a 1671 edition was published in Amsterdam by Johannes van Waesbergen. The work was the first to discuss the topography, archeology and history of the Lazio region. It was based partly on Kircher's extensive walks in the countryside around Rome, although it included sites that he had probably not visited in person.
The maps in the book were the work of Innocenzo Mattei. The book also reused a number of earlier illustrations from previously published works, by Étienne Dupérac, Daniele Stoopendahl and Matteo Greuter.
Kircher, scholar, born in Geisa, near Fulda, May 12, 1602, died in Rome Nov. 28, 1680. He entered the Society of Jesus on October 2, 1618. He was teaching philosophy and mathematics in Würzburg, when the victories of the Swedes in Germany forced him to take refuge first in France, in Avignon, then in Vienna, whence, in 1635, he was called to the chair of mathematics in the Collegio Romano.
Kircher entered the Society of Jesus on October 2, 1618. He was teaching philosophy and mathematics in Würzburg, when the victories of the Swedes in Germany forced him to take refuge first in France, in Avignon, then in Vienna, whence, in 1635, he was called to the chair of mathematics in the Colleggio Romano. He dealt with philology (Prodromus coptus, Rome 1636; Lingua aegyptiaca restituta, 1643); physics (Ars Magnesia, Würzburg 1631; Specula melitensis, Naples 1638; Ars magnae lucis et umbrae, Rome 1645); sacred liturgy (Rituale Ecclesiae aegyptiacae, Rome 1647); of astronomy (Itinerarium extaticum, Rome 1655); of natural history (Mundus subterraneus, Amsterdam 1665); of mathematics (Organum mathematicum, Würzburg 1668); of music (Musurgia universalis, Rome 1660; Phonurgia nova, Kempten 1673) and more. He also attempted Egyptology, to which belong the three volumes entitled Oedipus Aegyptiacus (Rome 1652), with which he believed he had discovered the key to the interpretation of hieroglyphics. Turning to the study of Chinese civilization he gave birth to China monumentis qua sacris qua profanis... illustrata (Rome 1667). Kircher also has a notable place in the history of geographic science, not so much for the bold and often abstruse hypotheses he formulated (especially in Mundus subterraneus) to explain certain physical phenomena, such as the surface and subterranean circulation of water, but for the indigestible and unelaborated collection of data and facts about distant countries that he had from Jesuit travelers and missionaries; to him is due the credit of having outlined the first sketch of a map of sea currents, and also that of having called attention to the phenomena, which today we say karst, although he collected and divulged in this respect many fantastic and extravagant reports, which, moreover, were generally believed in his time. Kircher is also the author of chorographic works of a historical-geographical nature, among which the most notable is perhaps his Latium (1671). He was also a diligent collector of classical, Christian, Oriental and South American antiquities. Of the relics he collected, the museum that bears his name was formed and is preserved in the Roman College (Kircherian Museum, now the Prehistoric and Ethnographic Museum).
Etching, in excellent condition.
Bibliografia
Harry B. Evans (2012). Exploring the Kingdom of Saturn: Kircher's Latium and Its Legacy; Brunet III, 667; Cicognara 3758; Graesse IV, 21; Sommervogel IV, 1067.
Athanasius KIRCHER (Geisa 1601 circa - Roma 1680)
|
German Jesuit educated in Fulda, was one of the most remarkable men of his time, seemingly interested in every aspect of life. He was an expert on China and its languages; Egypt and Ethiopia and the source of the Nile; he translated oriental scripts and hieroglyphics; made a scientific study of the evolution of the earth and its physical features; he wrote a treatise on the reasons of magnetic compass variations; and, in the middle of all of that, found time to invent the magic lantern, for which he is probably best remembered. Maps in his book Mundus Subterraneus were the first to describe tides and ocean currents beside showing the sites of all volcanoes known at that time.
|
Athanasius KIRCHER (Geisa 1601 circa - Roma 1680)
|
German Jesuit educated in Fulda, was one of the most remarkable men of his time, seemingly interested in every aspect of life. He was an expert on China and its languages; Egypt and Ethiopia and the source of the Nile; he translated oriental scripts and hieroglyphics; made a scientific study of the evolution of the earth and its physical features; he wrote a treatise on the reasons of magnetic compass variations; and, in the middle of all of that, found time to invent the magic lantern, for which he is probably best remembered. Maps in his book Mundus Subterraneus were the first to describe tides and ocean currents beside showing the sites of all volcanoes known at that time.
|