
| Reference: | MS3533 |
| Author | Alexis Hubert JAILLOT |
| Year: | 1692 ca. |
| Zone: | Africa |
| Printed: | Amsterdam |
| Measures: | 880 x 670 mm |


| Reference: | MS3533 |
| Author | Alexis Hubert JAILLOT |
| Year: | 1692 ca. |
| Zone: | Africa |
| Printed: | Amsterdam |
| Measures: | 880 x 670 mm |
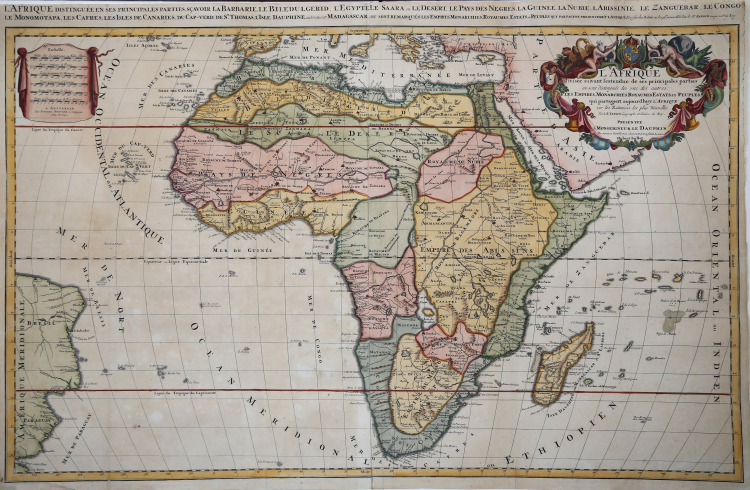
Fine map of Africa with a decorative title and scale cartouche.
Alexis-Hubert Jaillot (1632-1712), was a French cartographer. He joined the Sanson heirs and redrew Nicolas Sanson's maps on a larger scale. 'Atlas Nouveau' (1674), sea-atlas ' Le Neptune François' (1693).
This plate is from the newly engraved Dutch counterfeited edition of the ' Atlas Nouveau', published by Pieter Mortier in Amsterdam.
|
R. L. Betz "The Mapping of Africa…" (2007), map 118; O. I. Norwich, "Norwich's Maps of Africa", map 46
|
Alexis Hubert JAILLOT (1632 - 1712)
|
Alexis Hubert Jaillot (c. 1632- 1712) followed Nicholas Sanson (1600 - 1667) and his descendants in ushering in the great age of French Cartography in the late 17th and 18th century. The publishing center of the cartographic world gradually transitioned from Amsterdam to Paris following the disastrous inferno that destroyed the preeminent Blaeu firm in 1672. Hubert Jaillot was born in Franche-Comte and trained as a sculptor. When he married the daughter of the enlumineur de ala Reine, Nicholas Berey, he found himself positioned to inherit a lucrative map and print publishing firm. When Nicholas Sanson, the premier French cartographer of the day, died Jaillot negotiated with his heirs to republish much of Sanson's work. Though not a cartographer himself, Jaillot's access to the Sanson plates enabled him to publish numerous maps and atlases with only slight modifications and updates to the originals. As a sculptor and an artist, Jaillot's maps were particularly admired for their elaborate and meaningful allegorical title cartouches and other decorative elements. Jaillot used his allegorical cartouche work to extol the virtues of the Sun King Louis IV, and his military and political triumphs. These earned him the patronage of the French crown who used his maps in the tutoring of the young Dauphin. In 1686 he was awarded the title of Geographe du Roi< and with it significant prestige and the coveted yearly stipend of 600 Livres. Jaillot was one of the last French map makers to acquire this title. Louis XV, after taking the throne, replaced the position with the more prestigious and singular title of Premier Geographe du Roi. Jaillot died in Paris in 1712. His most important work was his 1693 Le Neptune Francois Jalliot was succeed by his son, Bernard Jean Hyacinthe Jaillot (1673-1739), grandson, Bernard Antoine Jaillot (???? – 1749) and the latter's brother-in-law, Jean Baptiste-Michel Renou de Chauvigné-Jaillot (1710-1780).
|
|
R. L. Betz "The Mapping of Africa…" (2007), map 118; O. I. Norwich, "Norwich's Maps of Africa", map 46
|
Alexis Hubert JAILLOT (1632 - 1712)
|
Alexis Hubert Jaillot (c. 1632- 1712) followed Nicholas Sanson (1600 - 1667) and his descendants in ushering in the great age of French Cartography in the late 17th and 18th century. The publishing center of the cartographic world gradually transitioned from Amsterdam to Paris following the disastrous inferno that destroyed the preeminent Blaeu firm in 1672. Hubert Jaillot was born in Franche-Comte and trained as a sculptor. When he married the daughter of the enlumineur de ala Reine, Nicholas Berey, he found himself positioned to inherit a lucrative map and print publishing firm. When Nicholas Sanson, the premier French cartographer of the day, died Jaillot negotiated with his heirs to republish much of Sanson's work. Though not a cartographer himself, Jaillot's access to the Sanson plates enabled him to publish numerous maps and atlases with only slight modifications and updates to the originals. As a sculptor and an artist, Jaillot's maps were particularly admired for their elaborate and meaningful allegorical title cartouches and other decorative elements. Jaillot used his allegorical cartouche work to extol the virtues of the Sun King Louis IV, and his military and political triumphs. These earned him the patronage of the French crown who used his maps in the tutoring of the young Dauphin. In 1686 he was awarded the title of Geographe du Roi< and with it significant prestige and the coveted yearly stipend of 600 Livres. Jaillot was one of the last French map makers to acquire this title. Louis XV, after taking the throne, replaced the position with the more prestigious and singular title of Premier Geographe du Roi. Jaillot died in Paris in 1712. His most important work was his 1693 Le Neptune Francois Jalliot was succeed by his son, Bernard Jean Hyacinthe Jaillot (1673-1739), grandson, Bernard Antoine Jaillot (???? – 1749) and the latter's brother-in-law, Jean Baptiste-Michel Renou de Chauvigné-Jaillot (1710-1780).
|