

| Reference: | S20984 |
| Author | Giovanni Antonio MAGINI |
| Year: | 1607 ca. |
| Zone: | Bologna |
| Printed: | Bologna |
| Measures: | 472 x 350 mm |


| Reference: | S20984 |
| Author | Giovanni Antonio MAGINI |
| Year: | 1607 ca. |
| Zone: | Bologna |
| Printed: | Bologna |
| Measures: | 472 x 350 mm |
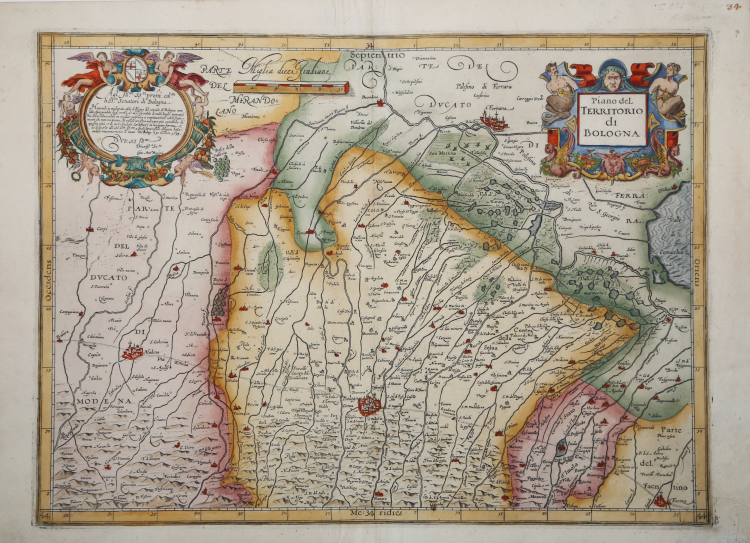
Map taken from L'Italia edited by Fabio Magini, published in Bologna in 1620, three years after the untimely death of his father.
Composed of a short descriptive text of only 24 pages, the work is accompanied by 61 maps of the peninsula, and is the first example of an Italian atlas. The work is entirely by the hand of Giovanni Antonio Magini, who began the realization of the maps in 1594 or so; the first dated map (1595) the map of the territory of Bologna. All the maps were printed before 1620, in their provisional drafts, later corrected and updated for the final edition. For the realization of the plates Magini used two of the most famous engravers of the time: the Belgian Arnoldo Arnoldi and the English Benjamin Wright.
In alto, nel cartiglio a destra, il titolo: Piano del TERRITORIO DI BOLOGNA, al centro la scala grafica Miglia dieci Italiane (10 miglia pari a mm 78). Nel cartiglio a sinistra sormontato dallo stemma della città la dedica Agl’Ill.mi SS.ri p[ad]roni col.mi li SS.ri Senatori di Bologna. Havendo io migliorato assai il disegno del contado di Bologna non solo espurgandolo dagl’errori, & accrescendolo di molti luoghi mancanti ma anco riducendolo in miglior positura et continuatione con li stati vicini che non era prima, ho voluto un'altra volta per più commodo di questa città et de tutti i studiosi darlo fuori in maggior forma, et dedicarlo alle SS.VV. Ill.me a quali sono tanto obligato basciandole riverentemente le mani. Di Bolog: li 10 Gen[n]aro 1599. D.V.SS Ill.me Divotiss.o Ser.re Gio Ant.o Magini. Orientazione nei quattro lati al centro con il nome dei punti cardinali Septentrio, Meridies, Oriens, Occidens, il nord in alto . Graduazione ai margini di 1’ in 1’ da 44° 3’ 30’’ a 44° 41’ di latitudine, e da 33° 23’ a 34° 37’ di longitudine.
Incisione in rame, finemente colorata a mano, in ottimo stato di conservazione. Iniziata da Arnoldo Arnoldi, la lastra venne probabilmente terminata dal Wright intorno al 1607.
Bibliografia
Almagià (1960): p. 22, tav. XXXVII; Dante Cremonini, L’Italia nelle vedute e carte geografiche dal 1493 al 1894 libri di viaggi e atlanti, 1996, p.28. Alberto Alberghini, Ferrara. La storia di un territorio in una collezione di mappe e vedute dal XV al XX secolo, 2008, p.13. Marco Petrella, Chiara Santini, Stefano Torresani, Geografie di un territorio. Studi e ricerche per un Dizionario storico dei cartografi in Emilia-Romagna, 2006, copertina e p.18. Stefano Torresani, "'Il particolare' ed 'il generale': topografia e corografie del Bolognese in età moderna" in Anna-Maria Guccini (a cura di), Memoria disegnata e territorio bolognese, Giornate di studi Mengoniani, Provincia di Bologna - Comune di Fontanelice, 2004, pp.34-39. Roberto Almagià, L’Italia di Giovanni Antonio Magini e la cartografia dell’Italia nei secoli XVI e XVII, 1922, pp.49-51. R.V. Tooley, Dictionary of Mapmakers, 1979, p.412. Franca Varignana (a cura di), Omaggio a Bologna materiali per un'immagine della città e del territorio, 1980, pp. 42 e 105.
Giovanni Antonio MAGINI (1555 - 1617)
|
Giovanni Antonio Magini was born in Padua in 1555, dedicating himself to the study of astronomy from an early age. In 1588 the Senate of Bologna appointed him Lecturer of Astronomy at the local University, choosing him instead of Galileo Galilei. His friendship with the Duke of Mantua, Vincenzo Gonzaga, helped Magini in his quest to obtain cartographical material for map-making from the various sovereigns ruling the different Italian states at that time. Because of Magini's early death in 1617, this effort was made famous by his son Fabio when he published the atlas "L'Italia" in Bologna in 1620. This is the first example of an Italian atlas and is made up of 24 pages of descriptive text and 61 maps of the Italian peninsula. Although this work was published posthumously, it can be entirely ascribed to Magini. He began drawing this maps around 1594, with the one depicting Bologna and its surrounding territories being the first. They were all printed before 1620 in draft editions which were then revised and updated for the final version. These draft proofs are extremely rare, although sometimes available for sale, and exhibit substantial differences in respect to the maps finally included in the atlas. Two of the most famous engravers of the time, Arnoldo Arnoldi and the englishman Benjamin Wright, were entrusted by Magini to engrave the plates. As we shall see in the presentation of the separate maps, they derive from different sources, both known and unknown, and therefore represent the result of an original work of critical analysis and compilation. This atlas had an important influence on the cartography of the italian peninsula for the following two centuries, beginning from Ortelius and going on to the principal dutch cartographers and editors.
|
Giovanni Antonio MAGINI (1555 - 1617)
|
Giovanni Antonio Magini was born in Padua in 1555, dedicating himself to the study of astronomy from an early age. In 1588 the Senate of Bologna appointed him Lecturer of Astronomy at the local University, choosing him instead of Galileo Galilei. His friendship with the Duke of Mantua, Vincenzo Gonzaga, helped Magini in his quest to obtain cartographical material for map-making from the various sovereigns ruling the different Italian states at that time. Because of Magini's early death in 1617, this effort was made famous by his son Fabio when he published the atlas "L'Italia" in Bologna in 1620. This is the first example of an Italian atlas and is made up of 24 pages of descriptive text and 61 maps of the Italian peninsula. Although this work was published posthumously, it can be entirely ascribed to Magini. He began drawing this maps around 1594, with the one depicting Bologna and its surrounding territories being the first. They were all printed before 1620 in draft editions which were then revised and updated for the final version. These draft proofs are extremely rare, although sometimes available for sale, and exhibit substantial differences in respect to the maps finally included in the atlas. Two of the most famous engravers of the time, Arnoldo Arnoldi and the englishman Benjamin Wright, were entrusted by Magini to engrave the plates. As we shall see in the presentation of the separate maps, they derive from different sources, both known and unknown, and therefore represent the result of an original work of critical analysis and compilation. This atlas had an important influence on the cartography of the italian peninsula for the following two centuries, beginning from Ortelius and going on to the principal dutch cartographers and editors.
|