



| Reference: | S35968 |
| Author | Vincenzo CORONELLI |
| Year: | 1688 ca. |
| Zone: | India |
| Printed: | Venice |
| Measures: | 500 x 670 mm |






| Reference: | S35968 |
| Author | Vincenzo CORONELLI |
| Year: | 1688 ca. |
| Zone: | India |
| Printed: | Venice |
| Measures: | 500 x 670 mm |
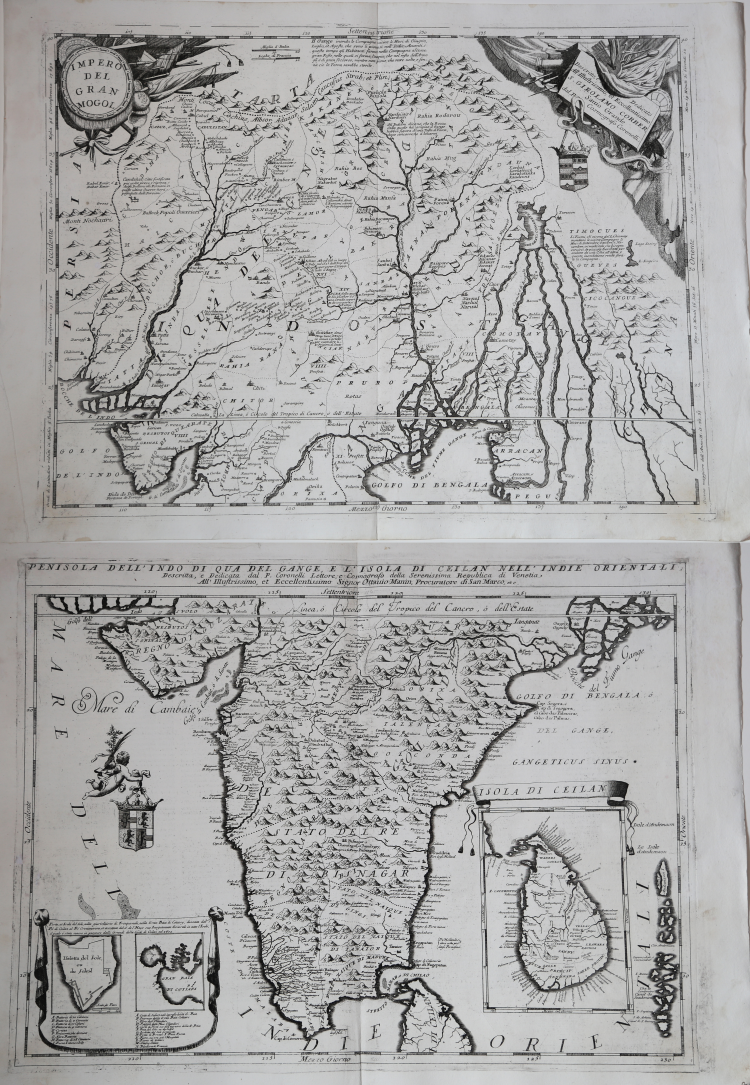
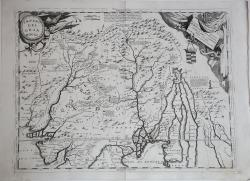
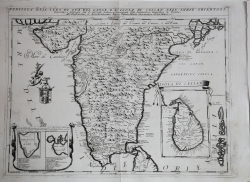
Impero del Gran Mogol & Penisola dell'Indo di qua del Gange e l'Isola di Ceilan nell'Indie Orientali descritta e dedicata dal P. Coronelli Lettore e Cosmografo della Serenissima Republica di Venetia all'Illustrissimo, et Eccellentissimo Signor Ottavio Manin, Procurator.
Two sheets map of India, taken from Coronelli's Isolario. Even printed separetely, the two sheets can be trimmed an joined.
The upper part is a beautiful and flamboyantly engraved large-scale map of Northern India at the time of the Mogul Empire. Also including Bangaledesh, Pakistan, Nepal and the Himalayas.
The map includes early place names as Kachemire, Iamba, Ragepor, Cabulistan, Kandauna, Harduari, Binsola, Burchar, etc.
On verso the globe gore showing Indochina by Coronelli, first published in the Libro dei Globi.
The lower part of the map shows India below the Tropic of Cancer, with insets of Sri Lanka and Trincomalee. The map is engraved in Coronelli's bold style with mountains and crisp detail filling the interior. The two insets are enclosed in decorative borders and the map is further embellished with a coat of arms held aloft by a cherub. Italian text on verso.
The map is taken from Isolario dell’Atlante Veneto del P. Coronelli, In Venetia MDCXCVI.
Coronelli lived a period of extraordinary editorial fecundity starting from 1689, when he had the chair of geography at the University at the Procuratie, with the publication, in 1690, of the first volume of the Atlante Veneto. Under the name of Atlante Veneto goes the entire collection of thirteen works composed over the next decade, from the Isolario to the Specchio del mare.
The Isolario aims, with a baroque and meticulous search for detail, to celebrate the possessions of the Serenissima. Monumental collection of maps and views of islands, represents the last of the "isolarios" conceived, which, between the end of the seventeenth and the beginning of the eighteenth century, were gradually supplanted by modern atlases, printed works characterized by increasing scientific precision and less and less artistic value. In the wake of the new colonial conquests, cartographic representations came to assume an increasingly technical character, until then rather arbitrary.
Very good condition.
Vincenzo CORONELLI (Venezia 1650 - 1718)
|
Cosmographer, geographer, biographer, encyclopedist, globe maker, inventor, expert of engeneering and hydraulics. Extraordinarily versatile mind and an extremely tireless man, he produced more than 140 pieces in different genres. At the age of 15, he entered the Franciscan Order, which he then guided as Gran Generale from 1699. He became famous as geographer and mathematician, awakening the interest in these subjects in Italy at the end of the XVII century. He travelled a lot, seeking for all that was new, and keeping a correspondance with the most important intellectuals of his time. In 1681 Louis XIV wanted him to go to France, to entrust him with the task of making two terraqueous globes (Marly Globes), with a diameter of 4 metres. Once he came back to Italy, in 1685, he became Cosmographer of the Venetian Republic, where he taught geography and founded the first geographic accademy, called The Argonauts Accademy. In his whole life he produced more that 500 maps; some of them can be found in his most famous works, such as the Venetian Atlas (1690), the Island Book of the Venetian Atlas (1696-97), the Book of Globes (1693). As far as his scientific method, he didn’t elaborate new cartographic systems, but followed the theories that were considered most popular and effective at his time, based on the Copernican system. The main characteristic of his charts is the high quantity of toponymic and historical information. In his most famous and dense work, the Venetian Atlas, we can find about 1100 plates, 200 of which are extremely technical and this is the reason why it is considered the first Italian atlas to describe and illustrate the whole world with charts and maps. It was published in 13 volumes, starting from 1690, and it took nearly ten years to finish it. It is divided in different parts, the most important are the Atlas itself, then the Island Book, the Corso Geografico and the Teatro delle città.
|
Vincenzo CORONELLI (Venezia 1650 - 1718)
|
Cosmographer, geographer, biographer, encyclopedist, globe maker, inventor, expert of engeneering and hydraulics. Extraordinarily versatile mind and an extremely tireless man, he produced more than 140 pieces in different genres. At the age of 15, he entered the Franciscan Order, which he then guided as Gran Generale from 1699. He became famous as geographer and mathematician, awakening the interest in these subjects in Italy at the end of the XVII century. He travelled a lot, seeking for all that was new, and keeping a correspondance with the most important intellectuals of his time. In 1681 Louis XIV wanted him to go to France, to entrust him with the task of making two terraqueous globes (Marly Globes), with a diameter of 4 metres. Once he came back to Italy, in 1685, he became Cosmographer of the Venetian Republic, where he taught geography and founded the first geographic accademy, called The Argonauts Accademy. In his whole life he produced more that 500 maps; some of them can be found in his most famous works, such as the Venetian Atlas (1690), the Island Book of the Venetian Atlas (1696-97), the Book of Globes (1693). As far as his scientific method, he didn’t elaborate new cartographic systems, but followed the theories that were considered most popular and effective at his time, based on the Copernican system. The main characteristic of his charts is the high quantity of toponymic and historical information. In his most famous and dense work, the Venetian Atlas, we can find about 1100 plates, 200 of which are extremely technical and this is the reason why it is considered the first Italian atlas to describe and illustrate the whole world with charts and maps. It was published in 13 volumes, starting from 1690, and it took nearly ten years to finish it. It is divided in different parts, the most important are the Atlas itself, then the Island Book, the Corso Geografico and the Teatro delle città.
|