



| Reference: | S369280 |
| Author | Dépôt des cartes et plans de la Marine |
| Year: | 1873 |
| Zone: | Taiwan |
| Printed: | Paris |
| Measures: | 990 x 650 mm |



| Reference: | S369280 |
| Author | Dépôt des cartes et plans de la Marine |
| Year: | 1873 |
| Zone: | Taiwan |
| Printed: | Paris |
| Measures: | 990 x 650 mm |
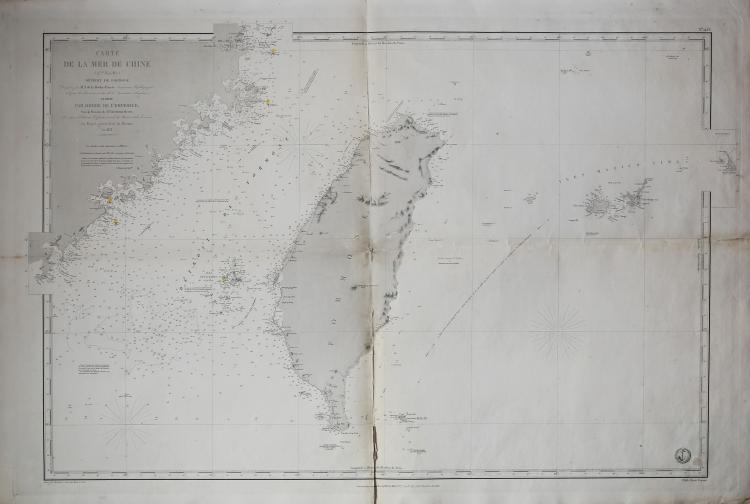
Large nautical chart of Taiwan, also known as Formosa Island, made by Ferdinand Antoine Jules de la Roche-Poncié in 1853.
The map is centered on Taiwan, but includes parts of Fujian, China, the Pescadores / Penghu Islands, and the Yaeyama Islands (Iles Majico Sima). This map was issued at a time when Taiwan was heavily in the news - headhunters of coruse - which can account for the issue and reissue of this chart from 1867 through the present 1873 edition.
The chart was made at the French Navy's chart depot (Depote de la Marine), which had started in 1720 with the acquisition of the Neptune François, a private cartographic business, whose materials went on to form the first nucleus of the Depot des cartes et plans under the direction of Captain De Luynes who was succeeded the following year by General Jacques Nicholas Bellin.
Ferdinand Antoine Jules de la Roche-Poncié (August 19, 1810 – March 30, 1881) was a French hydrographic engineer and cartographer active throughout the 19th century. Poncié was born in Vauxrenard, France. After graduating from the École Polytechnique in 1829 he joined the French navy, becoming a naval hydrographic engineer in 1832. Numerous important French surveys bear his name, including the first detailed hydrographic survey of the St. Pierre and Miquelon Islands, and numerous maps of East Asian waters. He received the Legion of Honor in 1841, ultimately attaining the grade of Commander. In 1860 he settled in Paris where he became a member of the Hydrographic Committee under Rear-Admiral Pierre Mathieu. He died in Paris in 1881.
Copperplate engraving, minimal flaws at center fold, otherwise in excellent condition.
Dépôt des cartes et plans de la Marine
|
The Dépôt de la Marine, known more formally as the Dépôt des cartes et plans de la Marine, was the central charting institution of France. The centralization of hydrography in France began in earnest when Jean-Baptiste Colbert became First Minister of France in 1661. Under his watch, the first Royal School of Hydrography began operating, as did the first survey of France’s coasts (1670-1689). In 1680, Colbert consolidated various collections of charts and memoirs into a single assemblage, forming the core of sources for what would become the Dépôt.
The Dépôt itself began as the central deposit of charts for the French Navy. In 1720, the Navy consolidated its collection with those government materials covering the colonies, creating a single large repository of navigation. By 1737, the Dépôt was creating its own original charts and, from 1750, they participated in scientific expeditions to determine the accurate calculation of longitude.
In 1773, the Dépôt received a monopoly over the composition, production, and distribution of navigational materials, solidifying their place as the main producer of geographic knowledge in France. Dépôt-approved charts were distributed to official warehouses in port cities and sold by authorized merchants. The charts were of the highest quality, as many of France’s premier mapmakers worked at the Dépôt in the eighteenth century, including Philippe Bauche, Jacques-Nicolas Bellin, Rigobert Bonne, Jean Nicolas Buache, and Charles-François Beautemps-Beaupré.
The Dépôt continued to operate until 1886, when it became the Naval Hydrographic Service. In 1971, it changed names again, this time to the Naval and Oceanographic Service (SHOM). Although its name has changed, its purpose is largely the same, to provide high quality cartographic and scientific information to the France’s Navy and merchant marine.
|
Dépôt des cartes et plans de la Marine
|
The Dépôt de la Marine, known more formally as the Dépôt des cartes et plans de la Marine, was the central charting institution of France. The centralization of hydrography in France began in earnest when Jean-Baptiste Colbert became First Minister of France in 1661. Under his watch, the first Royal School of Hydrography began operating, as did the first survey of France’s coasts (1670-1689). In 1680, Colbert consolidated various collections of charts and memoirs into a single assemblage, forming the core of sources for what would become the Dépôt.
The Dépôt itself began as the central deposit of charts for the French Navy. In 1720, the Navy consolidated its collection with those government materials covering the colonies, creating a single large repository of navigation. By 1737, the Dépôt was creating its own original charts and, from 1750, they participated in scientific expeditions to determine the accurate calculation of longitude.
In 1773, the Dépôt received a monopoly over the composition, production, and distribution of navigational materials, solidifying their place as the main producer of geographic knowledge in France. Dépôt-approved charts were distributed to official warehouses in port cities and sold by authorized merchants. The charts were of the highest quality, as many of France’s premier mapmakers worked at the Dépôt in the eighteenth century, including Philippe Bauche, Jacques-Nicolas Bellin, Rigobert Bonne, Jean Nicolas Buache, and Charles-François Beautemps-Beaupré.
The Dépôt continued to operate until 1886, when it became the Naval Hydrographic Service. In 1971, it changed names again, this time to the Naval and Oceanographic Service (SHOM). Although its name has changed, its purpose is largely the same, to provide high quality cartographic and scientific information to the France’s Navy and merchant marine.
|