



| Reference: | A48073 |
| Author | Willem Janszoon BLAEU |
| Year: | 1617 ca. |
| Zone: | Europe |
| Printed: | Amsterdam |
| Measures: | 565 x 415 mm |



| Reference: | A48073 |
| Author | Willem Janszoon BLAEU |
| Year: | 1617 ca. |
| Zone: | Europe |
| Printed: | Amsterdam |
| Measures: | 565 x 415 mm |
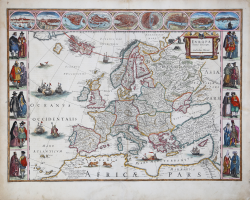
A striking and highly decorative map of Europe by Willem Jansz. Blaeu, produced at the height of the Golden Age of Dutch mapmaking. With decorative borders showing traditional costumes of European peoples and city views.
This is Schilder’s third state, still with the mythical island of Frisland to the southwest of Iceland. Decorated with a title cartouche, bears and lions on the land areas, and galleons and sea monsters on the sea.
The map is framed on both sides by five costumed figures. Along the upper edge runs a decorative border with nine European towns in oval frames: Amsterdam, Prague, Constantinople (Istanbul), Venice, Rome, Paris, London, Toledo and Lisbon. These borders are based entirely on border decorations from Blaeu's 1608 wall map of Europe. The geographical content is also a reduction of this wall map.
The map was first published separately in 1617, then added to Willem Blaeu's Atlantis Appendix in 1631. This example comes from the German edition of Theatrum Orbis Terrarum published by Willem's son Joan between 1644 and 1655. The later variant b without the imaginary island of Frisland between Iceland and Greenland appears in Joan Blaeu's Atlas Maior published 1662-72.
Willem Janszoon Blaeu was born 1571 in Alkmaar. He was trained from 1594 to 1596 by the famous danish astronomer Tycho Brahe. 1599 he went to Amsterdam and founded a business as globe maker. Later he started producing map and sea charts, including his first world map in 1605. In 1633 he was appointed Hydrographer for the Dutch East India Company (VOC). His most famous work was the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum sive Atlas Novus of 1635, which was published until 1655 in total six volumes. After Blaeu's death in 1638 his sons Joan and Cornelis continued the business and finished the Atlas Novus and started an even larger work, the Atlas Maior, which reached 12 volumes. In 1672 a fire destroyed the printing house and most of the printing plates. Joan Blaeu died the following year, leaving the business to his three sons Willem (1635-1701), Pieter (1637-1706) and Joan II (1650-1712). While the business began to decline in the hands of his sons, the dominance of the Blaeu publishing house finally ended in 1703 when the V.O.C. stopped publishing maps bearing the Blaeu family name. Some of the surviving plates were bought by F. de Wit and Schenk & Valk.
Etching with a fine later hand colour, a perfectly repaired tear at the lower white margin, otherwise good condition.
Bibliografia
Van der Krogt, P.: Koeman's Atlantes Neerlandici, 1000:2 variant a; Schilder, G.: Monumenta Cartographica Neerlandica VI, 26.3.
Willem Janszoon BLAEU (Uitgeest 1571- Amsterdam 1638)
|
At the beginning of the seventeenth century Amsterdam was becoming one of the wealthiest trading cities in Europe, the base of the Dutch East India Company and a centre of banking and diamond trades, its people noted for their intellectual skills and splendid craftsmanship.
At this propitious time in the history of the Northern Provinces, Willem Janszoon Blaeu, who was born at Alkmaar in 1571 and trained in astronomy and the sciences by Tycho Brahe, the celebrated Danish astronomer, founded a business in Amsterdam in 1599 as a globe and instrument maker.
It was not long before the business expanded, publishing maps, topographical works and books of sea charts as well as constructing globes.
His most notable early work was a map of Holland (1604), a fine World Map (1605-06) and Het Licht der Zeevaerdt (The Light of Navigation), a marine atlas, which went through many editions in different languages and under a variety of titles.
At the same time Blaeu was planning a major atlas intended to include the most up-to-date maps of the whole known world but progress on so vast a project was slow and not until he bought between 30 and 40 plates of the Mercator Atlas from Jodocus Hondius II to add to his own collection was he able to publish, in 1630, a 60-map volume with the title Atlantis Appendix.
It was another five years before the first two volumes of his planned world atlas, Atlas Novus or the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum were issued. About this time he was appointed Hydrographer to the East India Company.
In 1638 Willem Blaeu died and the business passed into the hands of his sons, Joan and Cornelis, who continued and expanded their father's ambitious plans.
After the death of Cornelis, Joan directed the work alone and the whole series of 6 volumes was eventually completed about 1655.
As soon as it was finished he began the preparation of the even larger work, the Atlas Major, which reached publication in 1662 in II volumes (later editions in 9-12 volumes) and contained nearly 6oo double-page maps and 3,000 pages of text.
This was, and indeed remains, the most magnificent work of its kind ever produced; perhaps its geographical content was not as up-to-date or as accurate as its author could have wished, but any deficiencies in that direction were more than compensated for by the fine engraving and colouring, the elaborate cartouches and pictorial and heraldic detail and especially the splendid calligraphy.
In 1672 a disastrous fire destroyed Blaeu's printing house in the Gravenstraat and a year afterwards Joan Blaeu died. The firm's surviving stocks of plates and maps were gradually dispersed, some of the plates being bought by F. de Wit and Schenk and Valck, before final closure in about 1695.
It ought to be mentioned here that there is often confusion between the elder Blaeu and his rival Jan Jansson (Johannes Janssonius). Up to about 1619 Blaeu often signed his works Guilielmus Janssonius or Willems Jans Zoon but after that time he seems to have decided on Guilielmus or G. Blaeu.
|
Willem Janszoon BLAEU (Uitgeest 1571- Amsterdam 1638)
|
At the beginning of the seventeenth century Amsterdam was becoming one of the wealthiest trading cities in Europe, the base of the Dutch East India Company and a centre of banking and diamond trades, its people noted for their intellectual skills and splendid craftsmanship.
At this propitious time in the history of the Northern Provinces, Willem Janszoon Blaeu, who was born at Alkmaar in 1571 and trained in astronomy and the sciences by Tycho Brahe, the celebrated Danish astronomer, founded a business in Amsterdam in 1599 as a globe and instrument maker.
It was not long before the business expanded, publishing maps, topographical works and books of sea charts as well as constructing globes.
His most notable early work was a map of Holland (1604), a fine World Map (1605-06) and Het Licht der Zeevaerdt (The Light of Navigation), a marine atlas, which went through many editions in different languages and under a variety of titles.
At the same time Blaeu was planning a major atlas intended to include the most up-to-date maps of the whole known world but progress on so vast a project was slow and not until he bought between 30 and 40 plates of the Mercator Atlas from Jodocus Hondius II to add to his own collection was he able to publish, in 1630, a 60-map volume with the title Atlantis Appendix.
It was another five years before the first two volumes of his planned world atlas, Atlas Novus or the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum were issued. About this time he was appointed Hydrographer to the East India Company.
In 1638 Willem Blaeu died and the business passed into the hands of his sons, Joan and Cornelis, who continued and expanded their father's ambitious plans.
After the death of Cornelis, Joan directed the work alone and the whole series of 6 volumes was eventually completed about 1655.
As soon as it was finished he began the preparation of the even larger work, the Atlas Major, which reached publication in 1662 in II volumes (later editions in 9-12 volumes) and contained nearly 6oo double-page maps and 3,000 pages of text.
This was, and indeed remains, the most magnificent work of its kind ever produced; perhaps its geographical content was not as up-to-date or as accurate as its author could have wished, but any deficiencies in that direction were more than compensated for by the fine engraving and colouring, the elaborate cartouches and pictorial and heraldic detail and especially the splendid calligraphy.
In 1672 a disastrous fire destroyed Blaeu's printing house in the Gravenstraat and a year afterwards Joan Blaeu died. The firm's surviving stocks of plates and maps were gradually dispersed, some of the plates being bought by F. de Wit and Schenk and Valck, before final closure in about 1695.
It ought to be mentioned here that there is often confusion between the elder Blaeu and his rival Jan Jansson (Johannes Janssonius). Up to about 1619 Blaeu often signed his works Guilielmus Janssonius or Willems Jans Zoon but after that time he seems to have decided on Guilielmus or G. Blaeu.
|