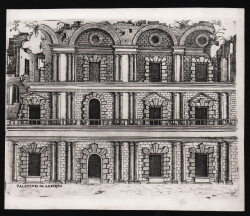
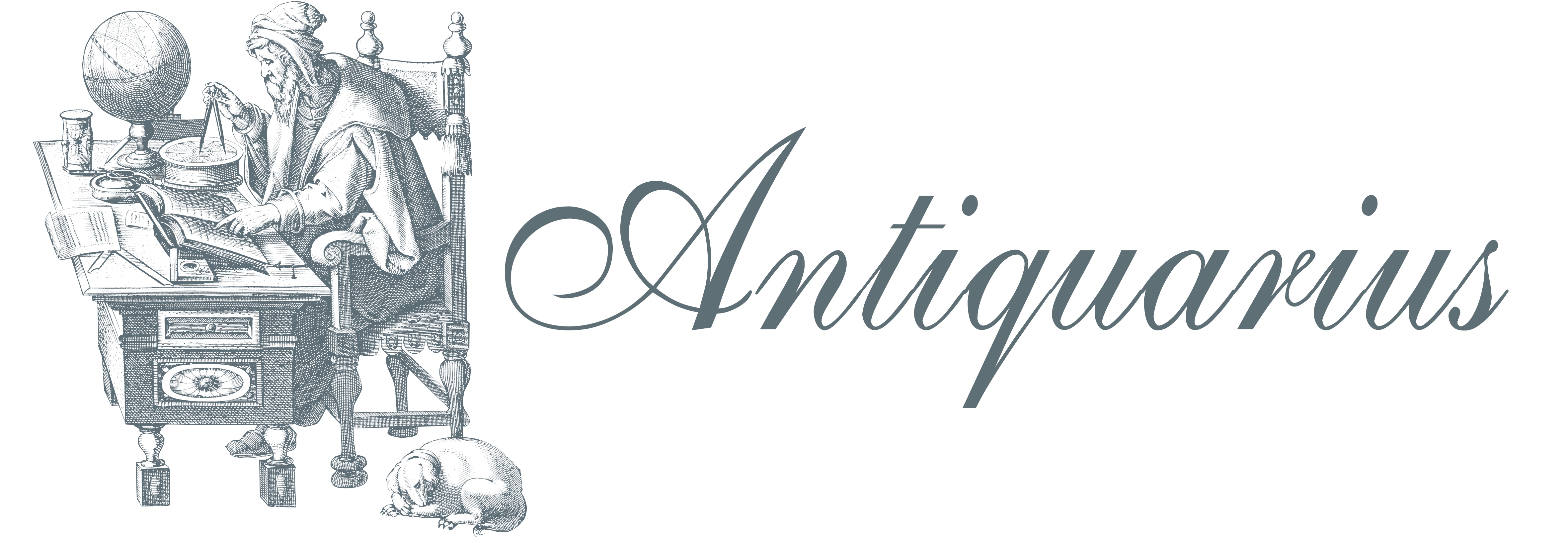Jupiter Temple Base
Monogrammista G.A. (Maestro del Trabocchetto)
Code:
S45067
Measures:
215 x 335 mm
Year:
1530 ca.
Printed:
Rome
Reconstruction of Agrippa's Palace
Monogrammista G.A. (Maestro del Trabocchetto)
Code:
S45062
Measures:
185 x 140 mm
Year:
1530 ca.
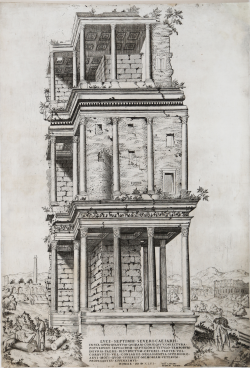
Reconstruction of Claudius' Palace
Monogrammista G.A. (Maestro del Trabocchetto)
Code:
S45061
Measures:
135 x 190 mm
Year:
1530 ca.
Victory of Scipio against Siface & Triumph of Scipio
Maestro B nel Dado
Code:
S45041
Measures:
255 x 440 mm
Year:
1535 ca.
Sheet with four column bases
Agostino de Musi detto VENEZIANO
Code:
S45066
Measures:
415 x 270 mm
Year:
1536
The Emperor Trajan offers a sacrifice
Leon DAVENT detto "Maestro L.D."
Code:
S10934
Measures:
472 x 267 mm
Year:
1545 ca.
IMP. CAES. LVCIO. SEPTIMIO. M. FIL. SEVERO...
Antonio LAFRERI
Code:
S45012
Measures:
400 x 440 mm
Year:
1547
The Roma Cesi or Allegory of Rome
Nicolas Beatrizet detto BEATRICETTO
Code:
S20850
Measures:
380 x 445 mm
Year:
1549
Veteris aquae Claudiæ ex Tiburtino forma
Antonio LAFRERI
Code:
S40217
Measures:
480 x 365 mm
Year:
1549
The Roma Cesi or Allegory of Rome
Nicolas Beatrizet detto BEATRICETTO
Code:
S45046
Measures:
390 x 490 mm
Year:
1549
Maccarani States Building (Cenci Palace)
Antonio LAFRERI
Code:
S45059
Measures:
420 x 325 mm
Year:
1549