


| Reference: | S45262 |
| Author | Vincenzo CORONELLI |
| Year: | 1689 ca. |
| Zone: | Malta |
| Printed: | Venice |
| Measures: | 607 x 460 mm |



| Reference: | S45262 |
| Author | Vincenzo CORONELLI |
| Year: | 1689 ca. |
| Zone: | Malta |
| Printed: | Venice |
| Measures: | 607 x 460 mm |
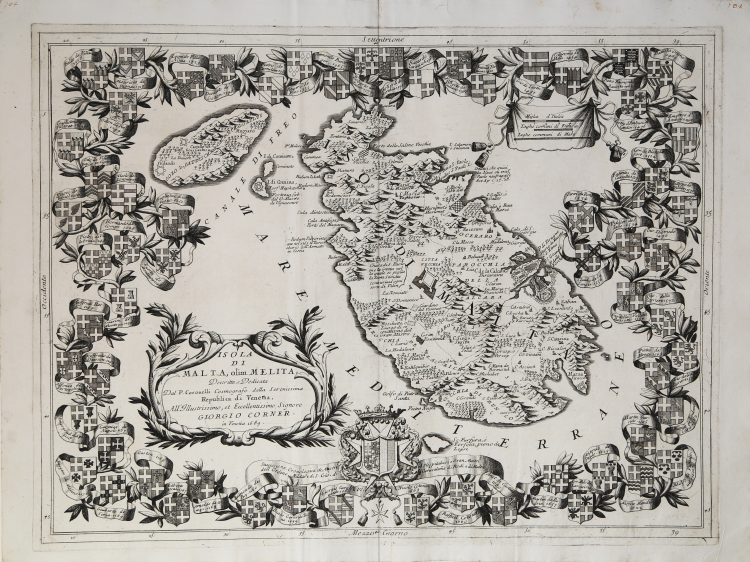
Isola di Malta olim Melita. Descritta, e Dedicata Dal P. Coronelli Cosmografo della Serenissima Republica di Venetia, All' Illustrissimo, et Eccelentissimo Signore Giorgio Corner in Venetia 1689.
Superbly ornate map of Malta and Gozo by Vincenzo Coronelli dated 1689. Published in Venice, the map is dedicated to Giorgio Corner, Bishop of Padua from 1643 until 1663 and a descendant of Doges of Venice. The map is richly decorated around its entire circumference with the coats of arms of the Grand Masters of the Order of St John of Jerusalem. The coats of arms are entwined with foliate decoration and ribbons containing the names and installation dates of the Grand Masters. Blank verso.
This map has highly detailed place names. The orientation is towards North with coordinates placed around the border of the map. The title of the map is within decorative cartouche. The map depicts the coats of arms of Grand Masters ‘Fra Gerardo’ to’Giorgio [sic] Caraffa’. Legend: Successione, Cronologica de Mastri Hospitalieri e Gran Mastri / dell Ordine Militare di S. Gio= di Gerusalem[m]e di Rodi e di Malta. Also larger coat of arms, possibly of Giorgio Corner.
The map is surrounded by 63 armorials of the Grand Masters of the Knights of Malta.
The Knights of Malta were initially founded as the Knights Hospitallers, a quasi-military order helping pilgrims in the Holy Land. Forced to leave after the failure of the crusades, the order moved from island to island in the Mediterranean before arriving in Malta in 1530. There they established their base, and from here, they campaigned against the Barbary Pirates, earning the wrath of the Ottoman Sultan. In 1565, the Sultan sent a force of some 40,000 men to capture Malta, but the order managed to hold out until relief came. When the replacement city was built, it was named Valetta after the Grand Master who conducted the defence, Jean de la Valette. After that, the Knights of Malta stayed there, secure until the French Revolution. In 1798 the French fleet sailed for shelter in Valetta and then turned on its host. Losing the island caused a diaspora and diminishing of the order, although it still exists today.
The map is taken from Corso geografico universale, o sia la terra divisa nelle sue parti e subdistinta ne' suoi gran regni. Esposta in tavole geografiche ricorrette et accresciute di tutte le nuove scoperte, ad uso dell'Accademia Cosmografica degli Argonauti dal Padre Maestro Vincenzo Coronelli M. C. Cosmografo della Serenissima Republica di Venetia. Dedicata alla Santità di Nostro Signore Innocenzo XII. P. I. In Venetia, a spese dell'autore. MDCXCII.
Coronelli lived a period of extraordinary editorial fecundity starting from 1689, when he had the chair of geography at the University at the Procuratie, with the publication, in 1690, of the first volume of the Atlante Veneto. Under the name of Atlante Veneto goes the entire collection of thirteen works composed over the next decade, from the Isolario to the Specchio del mare. Only some of these works can be defined as atlas, and are of very unequal value, since we go from original and fundamental works such as those mentioned or the Corso Geografico to works of compilation or simple collections of views. The Corso Geografico came out in several editions with different numbers of maps - sixty-eight maps in 1689-92; one hundred and seventy-three maps in 1692; two hundred and sixty maps in 1694-97 - which were also sold separately, at the rate of six a month for two years. The maps were alle engraved between 1688 and 1692 in the well-equipped cartographic workshop of the Frari convent, where foreign engravers also worked.
Copperplate, very good condition.
Bibliografia
Baynton-Williams New Worlds - p.110; Shirley (Brit.Lib.) - Vol.1 p. 433 T.Coro-13a (125)
Vincenzo CORONELLI (Venezia 1650 - 1718)
|
Cosmographer, geographer, biographer, encyclopedist, globe maker, inventor, expert of engeneering and hydraulics. Extraordinarily versatile mind and an extremely tireless man, he produced more than 140 pieces in different genres. At the age of 15, he entered the Franciscan Order, which he then guided as Gran Generale from 1699. He became famous as geographer and mathematician, awakening the interest in these subjects in Italy at the end of the XVII century. He travelled a lot, seeking for all that was new, and keeping a correspondance with the most important intellectuals of his time. In 1681 Louis XIV wanted him to go to France, to entrust him with the task of making two terraqueous globes (Marly Globes), with a diameter of 4 metres. Once he came back to Italy, in 1685, he became Cosmographer of the Venetian Republic, where he taught geography and founded the first geographic accademy, called The Argonauts Accademy. In his whole life he produced more that 500 maps; some of them can be found in his most famous works, such as the Venetian Atlas (1690), the Island Book of the Venetian Atlas (1696-97), the Book of Globes (1693). As far as his scientific method, he didn’t elaborate new cartographic systems, but followed the theories that were considered most popular and effective at his time, based on the Copernican system. The main characteristic of his charts is the high quantity of toponymic and historical information. In his most famous and dense work, the Venetian Atlas, we can find about 1100 plates, 200 of which are extremely technical and this is the reason why it is considered the first Italian atlas to describe and illustrate the whole world with charts and maps. It was published in 13 volumes, starting from 1690, and it took nearly ten years to finish it. It is divided in different parts, the most important are the Atlas itself, then the Island Book, the Corso Geografico and the Teatro delle città.
|
Vincenzo CORONELLI (Venezia 1650 - 1718)
|
Cosmographer, geographer, biographer, encyclopedist, globe maker, inventor, expert of engeneering and hydraulics. Extraordinarily versatile mind and an extremely tireless man, he produced more than 140 pieces in different genres. At the age of 15, he entered the Franciscan Order, which he then guided as Gran Generale from 1699. He became famous as geographer and mathematician, awakening the interest in these subjects in Italy at the end of the XVII century. He travelled a lot, seeking for all that was new, and keeping a correspondance with the most important intellectuals of his time. In 1681 Louis XIV wanted him to go to France, to entrust him with the task of making two terraqueous globes (Marly Globes), with a diameter of 4 metres. Once he came back to Italy, in 1685, he became Cosmographer of the Venetian Republic, where he taught geography and founded the first geographic accademy, called The Argonauts Accademy. In his whole life he produced more that 500 maps; some of them can be found in his most famous works, such as the Venetian Atlas (1690), the Island Book of the Venetian Atlas (1696-97), the Book of Globes (1693). As far as his scientific method, he didn’t elaborate new cartographic systems, but followed the theories that were considered most popular and effective at his time, based on the Copernican system. The main characteristic of his charts is the high quantity of toponymic and historical information. In his most famous and dense work, the Venetian Atlas, we can find about 1100 plates, 200 of which are extremely technical and this is the reason why it is considered the first Italian atlas to describe and illustrate the whole world with charts and maps. It was published in 13 volumes, starting from 1690, and it took nearly ten years to finish it. It is divided in different parts, the most important are the Atlas itself, then the Island Book, the Corso Geografico and the Teatro delle città.
|