

| Reference: | VR50FR |
| Author | Alexis Hubert JAILLOT |
| Year: | 1699 ca. |
| Zone: | Europe |
| Printed: | Paris |
| Measures: | 765 x 520 mm |


| Reference: | VR50FR |
| Author | Alexis Hubert JAILLOT |
| Year: | 1699 ca. |
| Zone: | Europe |
| Printed: | Paris |
| Measures: | 765 x 520 mm |
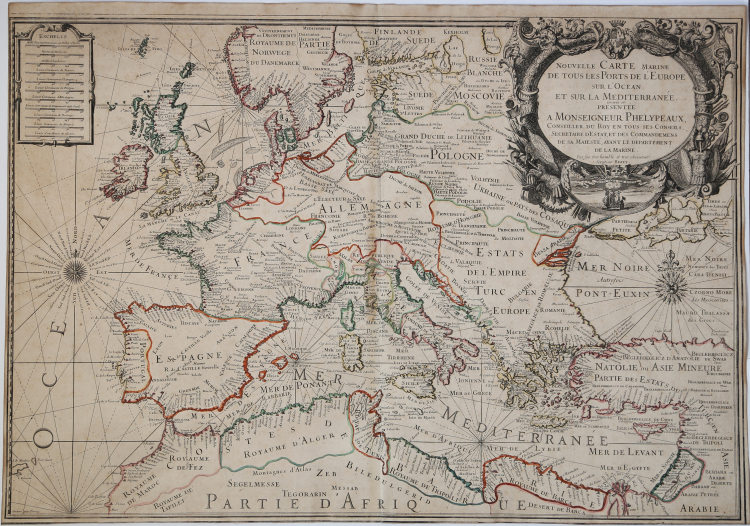
Nouvelle Carte Marine de tous les Ports de l’Europe sur l’Océan et la Méditerranée. Gravée et présentée à Monseigneur Phelypeaux, Conseiller du Roy en tous ses conseils, Secrétaire d’Estat, et des Commandemens de sa Maiesté, avant le Département de la Marine.
Etching, signed in the cartouche by the engraver Nicolas Berey II: Par son tres humble et tres obeissant Serviteur Berey. At lower left we find again the engraver's signature and the imprint A Paris Chés le S.r Jaillot Géographe ordinaire du Roy sur le Quay et a coté des grands Augustins.
A fine impression, of the first state of three, with contemporary outline colour, very good condition.
Taken from: Atlas François, contenant les cartes géographiques dans lesquelles sont très exactement remarquez les Empires, Monarchies, Royaumes et Estats de l’europe, de l’Asie, de l’Afrique et de l’Amerique […] à Hubert Jaillot, geographe ordinaire de sa Majesté.
Nautical chart of Europe, engraved by Claude Auguste Berey, whose signature appears both in the cartouche and in the lower left corner. The work is dedicated to Jérôme Phélypeaux de Pontchartrain (1674 - 1747), Secretary of State of the King and Secretary of State of the Navy from 6 September 1699 to 1 October 1715.
On the death of Nicolas II, Alexis Hubert Jaillot took over as head of the printing house Berey. This skilled businessman was born around 1632 in Avignon-lès-Saint-Claude. Since childhood Jaillot had shown a good talent for art and drawing and had learned sculpture from his brother Pierre-Simón. During the Franco-Spanish conflict their hometown was devastated, and so the two brothers moved to Paris in 1657. There they soon acquired a certain reputation and the title of "Sculpteur du Roy". In 1665, Jaillot married with Jeanne Berey, daughter of Nicolas I Berey. Jaillot's fortune was to enter the cartographic market at a particularly favorable time. At the beginning of 1668, under Louis XIV, a particularly fruitful period began for France, as a consequence of the constant territorial expansion there was a great demand for maps that represented French conquests and new frontiers.
Later, Jaillot joined forces with the sons of Nicolas Sanson, and was able to market new maps with the prestigious Sanson name. His Atlas of 1681, the "Atlas Nouveau", became such a commercial success that it was illegally copied by other publishers.
Jaillot cannot be counted among the cartographers of the time such as the Sansons and Duval, but he was a skilled engraver who was able to intelligently exploit the resources he had inherited, making them wonderful works. His fame grew to the point that on 20 July 1686 he was named "Géographe du Roy" and was given a large annual pension; the title allowed him to defend himself against numerous counterfeiters.
One of his most beautiful works was "Le Neptune François, or Atlas Nouveau des Cartes Marine". From the beginning of the eighteenth century its map production decreased: more and more updated maps were required which it was not able to offer; Jaillot (d. 1712) ceded, therefore, the company to his son Bernard Jean-Hyacinthe.
Claude Auguste Berey (1651 - 1732) was a master calligrapher writer, engraver and dealer of French prints; second son of Nicolas I Berey and his second wife Marie Trémison and half-brother of Nicolas II Berey (1640 - 1667), he later worked for Alexis-Hubert Jaillot. Active between 1690 and 1730, Claude Auguste himself engraved several plates for "Le Neptune François, or Atlas Nouveau des Cartes Marine".
Around 1697 he had a print shop in the rue Saint-Jacques, under the banner of the Princess of Savoy.
Themap can be dated to 1699 - 1700, as soon as Phélypeaux was commissioned; some examples of the work show, in the lower left corner, the imprint: Se Vend a Paris chez Iaillot le fils sur le Quay de l'Orloge du Palais; these are the runs of Bernard Jean-Hyacinthe Jaillot. The map had a further reprint from Louis Denis's typography.
Bibliografia: Mare Nostrum, a historic voyage across the Mediterranean Sea, Lussemburgo, 2003, p. 36; National Maritime Museum, Catalogue of the Library - Vol. Three, Atlas & Cartography, Londra, 1971, pp. 284-285, n. 240 (72); M. Pastoureau, Les Atlas Francais XVIe-XVIIe siècles, Parigi, 1984, pp. 229-292.
|
S. Bifolco, "Mare Nostrum, Cartografia nautica a stampa del Mar Mediterraneo" (2020), pp. 248-249, tav. 115.
|
Alexis Hubert JAILLOT (1632 - 1712)
|
Alexis Hubert Jaillot (c. 1632- 1712) followed Nicholas Sanson (1600 - 1667) and his descendants in ushering in the great age of French Cartography in the late 17th and 18th century. The publishing center of the cartographic world gradually transitioned from Amsterdam to Paris following the disastrous inferno that destroyed the preeminent Blaeu firm in 1672. Hubert Jaillot was born in Franche-Comte and trained as a sculptor. When he married the daughter of the enlumineur de ala Reine, Nicholas Berey, he found himself positioned to inherit a lucrative map and print publishing firm. When Nicholas Sanson, the premier French cartographer of the day, died Jaillot negotiated with his heirs to republish much of Sanson's work. Though not a cartographer himself, Jaillot's access to the Sanson plates enabled him to publish numerous maps and atlases with only slight modifications and updates to the originals. As a sculptor and an artist, Jaillot's maps were particularly admired for their elaborate and meaningful allegorical title cartouches and other decorative elements. Jaillot used his allegorical cartouche work to extol the virtues of the Sun King Louis IV, and his military and political triumphs. These earned him the patronage of the French crown who used his maps in the tutoring of the young Dauphin. In 1686 he was awarded the title of Geographe du Roi< and with it significant prestige and the coveted yearly stipend of 600 Livres. Jaillot was one of the last French map makers to acquire this title. Louis XV, after taking the throne, replaced the position with the more prestigious and singular title of Premier Geographe du Roi. Jaillot died in Paris in 1712. His most important work was his 1693 Le Neptune Francois Jalliot was succeed by his son, Bernard Jean Hyacinthe Jaillot (1673-1739), grandson, Bernard Antoine Jaillot (???? – 1749) and the latter's brother-in-law, Jean Baptiste-Michel Renou de Chauvigné-Jaillot (1710-1780).
|
|
S. Bifolco, "Mare Nostrum, Cartografia nautica a stampa del Mar Mediterraneo" (2020), pp. 248-249, tav. 115.
|
Alexis Hubert JAILLOT (1632 - 1712)
|
Alexis Hubert Jaillot (c. 1632- 1712) followed Nicholas Sanson (1600 - 1667) and his descendants in ushering in the great age of French Cartography in the late 17th and 18th century. The publishing center of the cartographic world gradually transitioned from Amsterdam to Paris following the disastrous inferno that destroyed the preeminent Blaeu firm in 1672. Hubert Jaillot was born in Franche-Comte and trained as a sculptor. When he married the daughter of the enlumineur de ala Reine, Nicholas Berey, he found himself positioned to inherit a lucrative map and print publishing firm. When Nicholas Sanson, the premier French cartographer of the day, died Jaillot negotiated with his heirs to republish much of Sanson's work. Though not a cartographer himself, Jaillot's access to the Sanson plates enabled him to publish numerous maps and atlases with only slight modifications and updates to the originals. As a sculptor and an artist, Jaillot's maps were particularly admired for their elaborate and meaningful allegorical title cartouches and other decorative elements. Jaillot used his allegorical cartouche work to extol the virtues of the Sun King Louis IV, and his military and political triumphs. These earned him the patronage of the French crown who used his maps in the tutoring of the young Dauphin. In 1686 he was awarded the title of Geographe du Roi< and with it significant prestige and the coveted yearly stipend of 600 Livres. Jaillot was one of the last French map makers to acquire this title. Louis XV, after taking the throne, replaced the position with the more prestigious and singular title of Premier Geographe du Roi. Jaillot died in Paris in 1712. His most important work was his 1693 Le Neptune Francois Jalliot was succeed by his son, Bernard Jean Hyacinthe Jaillot (1673-1739), grandson, Bernard Antoine Jaillot (???? – 1749) and the latter's brother-in-law, Jean Baptiste-Michel Renou de Chauvigné-Jaillot (1710-1780).
|