


| Reference: | mms1040 |
| Author | Johannes JANSSONIUS |
| Year: | 1640 ca. |
| Zone: | Bermuda |
| Printed: | Amsterdam |
| Measures: | 520 x 400 mm |



| Reference: | mms1040 |
| Author | Johannes JANSSONIUS |
| Year: | 1640 ca. |
| Zone: | Bermuda |
| Printed: | Amsterdam |
| Measures: | 520 x 400 mm |
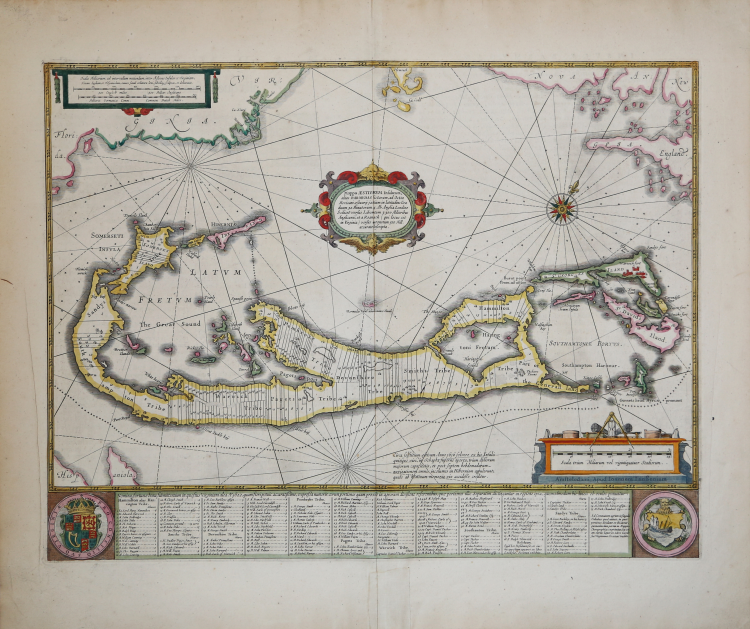
The map shows the island divided into tribes and lots, and below the map itself appear the coats of arms of Bermuda and England and the names of the first proprietors and the number of shares assigned each. A most attractive variant on the Norwood survey map.
The ‘Sea Venture’ under Sir George Somers was wrecked off Bermuda in 1609 and the surviving Englishmen divided the island into Tribes (later Parishes) and Shares, which are individually listed with their owners at the foot of the map. The map's Latin title, Mappa Aestivarum Insularum, means Summer (or Somers) Island for its first leader.
Shortly afterwards the Bermudas were granted to the Virginia Company, hence various references to the Company on the map including the distance to the Roanoke Colony in Virginia.
The miniature map with its own scale, top left, shows the island’s position relative to the Virginian coast.
Jansson derived his map from Richard Norwood’s survey which was carried out in 1622 and published by John Speed in 1627. It remains one of the most accurate and decorative maps of the period.
Johannes Janssonius (Arnhem, 1588-1664), son of the Arnhem publisher Jan Janssen, married Elisabeth Hondius, daughter of Jodocus Hondius, in Amsterdam in 1612. After his marriage, he settled down in this town as a bookseller and publisher of cartographic material. In 1618 he established himself in Amsterdam next door to Blaeu’s book shop. He entered into serious competition with Willem Jansz. Blaeu.. His activities not only concerned the publication of atlases and books, but also of single maps and an extensive book trade with branches in Frankfurt, Danzig, Stockholm, Copenhagen, Berlin, Koningsbergen, Geneva, and Lyon. In 1631 he began publishing atlases together with Henricus Hondius. In the early 1640s Henricus Hondius left the atlas publishing business completely to Janssonius. Competition with Joan Blaeu, Willem’s son and successor, in atlas production prompted Janssonius to enlarge his Atlas Novus finally into a work of six volumes, into which a sea atlas and an atlas of the Old World were inserted. After the death of Joannes Janssonius, the shop and publishing firm were continued by the heirs under the direction of Johannes van Waesbergen (c. 1616-1681), son-in-law of Joannes Janssonius. The copperplates from Janssonius’s atlases were afterwards sold to Schenk and Valck.
Copperplate, original outline colour, in good condition.
|
Palmer/Tooley, The mapping of Bermuda, plate XI.
|
Johannes JANSSONIUS (1588-1664)
|
Johannes Janssonius, more commonly known to us as Jan Jansson, was born in Arnhem where his father was a bookseller and publisher (Jan Janszoon the Elder). In 1612 he married the daughter of the cartographer and publisher Jodocus Hondius, and then set up in business in Amsterdam as a book publisher. In 1616 he published his first maps of France and Italy and from then onwards he produced a very large number of maps, perhaps not quite rivalling those of the Blaeu family but running a very close second in quantity and quality. From about 1630 to 1638 he was in partnership with his brother-in-law, Henricus Hondius, issuing further editions of the Mercator/Hondius atlases to which his name was added. On the death of Henricus he took over the business, expanding the atlas still further, until eventually he published an 11-volume Atlas Major on a scale similar to Blaeu's Atlas Major.
The first full edition of Jansson's English County Maps was published in 1646 but some years earlier he issued a number of British maps in the Mercator/Hondius/Jansson series of atlases (1636-44); the maps were printed from newly engraved plates and are different from the later 1646 issue and are now rarely seen (see Appendix B for further details).
In general appearance Jansson's maps are very similar to those of Blaeu and, in fact, were often copied from them, but they tend to be more flamboyant and, some think, more decorative.
After Jansson's death his heirs published a number of maps in an Atlas Contractus in 1666 and later still many of the plates of his British maps were acquired by Pieter Schenk and Gerard Valck, who published them again in 1683 as separate maps.
|
|
Palmer/Tooley, The mapping of Bermuda, plate XI.
|
Johannes JANSSONIUS (1588-1664)
|
Johannes Janssonius, more commonly known to us as Jan Jansson, was born in Arnhem where his father was a bookseller and publisher (Jan Janszoon the Elder). In 1612 he married the daughter of the cartographer and publisher Jodocus Hondius, and then set up in business in Amsterdam as a book publisher. In 1616 he published his first maps of France and Italy and from then onwards he produced a very large number of maps, perhaps not quite rivalling those of the Blaeu family but running a very close second in quantity and quality. From about 1630 to 1638 he was in partnership with his brother-in-law, Henricus Hondius, issuing further editions of the Mercator/Hondius atlases to which his name was added. On the death of Henricus he took over the business, expanding the atlas still further, until eventually he published an 11-volume Atlas Major on a scale similar to Blaeu's Atlas Major.
The first full edition of Jansson's English County Maps was published in 1646 but some years earlier he issued a number of British maps in the Mercator/Hondius/Jansson series of atlases (1636-44); the maps were printed from newly engraved plates and are different from the later 1646 issue and are now rarely seen (see Appendix B for further details).
In general appearance Jansson's maps are very similar to those of Blaeu and, in fact, were often copied from them, but they tend to be more flamboyant and, some think, more decorative.
After Jansson's death his heirs published a number of maps in an Atlas Contractus in 1666 and later still many of the plates of his British maps were acquired by Pieter Schenk and Gerard Valck, who published them again in 1683 as separate maps.
|