

| Reference: | MS4332 |
| Author | Vincent Tofiño de San Miguel |
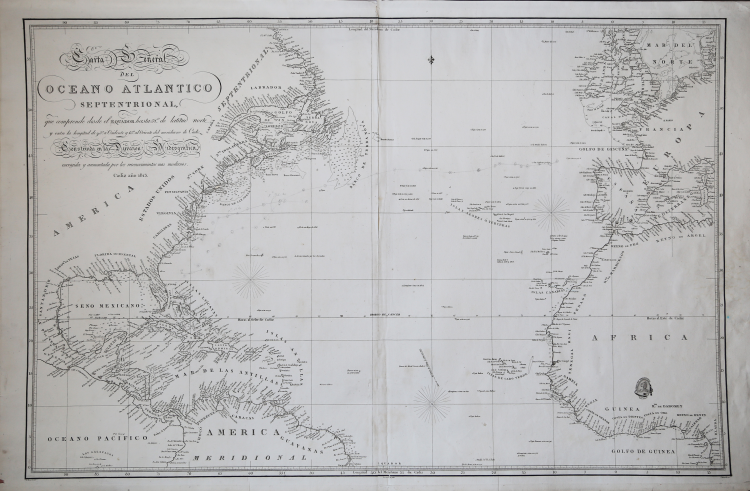
| Year: | 1813 |
| Zone: | Atlantic Sea |
| Printed: | Cadiz |
| Measures: | 970 x 610 mm |


| Reference: | MS4332 |
| Author | Vincent Tofiño de San Miguel |
| Year: | 1813 |
| Zone: | Atlantic Sea |
| Printed: | Cadiz |
| Measures: | 970 x 610 mm |
Carta General del Oceano Atlántico Septentrional que comprende desde el Ecuador hasta 58º 35' de latitud norte, y entre la longitud de 93º 45' al Oeste, 17º al Este del meridiano de Cádiz; España Dirección de Hidrografía, entidad productora; José Espejo, dibujante; Clemente Noguera, grabador; Manuel Giraldós, grabador texto; 1837.
Nautical chart of the Atlantic by Vincent Tofino de San Miguel, printed by DIRECCION HIDROGRAFICA DE MADRID.
Etching, good condition. Rare.
Vincent Tofiño de San Miguel (Cadice 1732 - 1795 San Fernando)
|
Vicente Tofiño de San Miguel y Wanderiales (or Vanderiales) was a Spanish navigator and cosmographer. He studied experimental physics and then joined the army, which he subsequently left. In 1755 Jorge Juan asked Tofiño to join the faculty of the Academy of Marines at Cádiz (Academia de Guardia Marinas de Cádiz) as a mathematics instructor, while also allowing Tofiño to join the Armada as a second lieutenant (alférez de navío). In 1768 Tofiño was named Director of the Academy and in 1773, was named Director of the Academies of Ferrol and Cartagena as well. He participated in the expeditions against Algiers (1773) and the Great Siege of Gibraltar (1782). He acquired the rank of Brigadier of the Armada in 1784, and in 1789 the rank of Rear Admiral.
He planned the initial construction, and worked at, the Royal Institute and Observatory of the Armada (Real Instituto y Observatorio de la Armada) of the Company of Marines, publishing observations with great scientific skill, like the transit of Venus by the Sun, taking advantage of an eclipse on 3 June 1796.
Tofiño went to sea and the result of this was several works, including Derrotero de las costas de España en el mar Mediterráneo y África (1787) (Pilot's Log-book of the Coasts of Spain in the Mediterranean Sea and Africa); his colección de cartas esféricas de las costas de España y África... (1788) (Collection of Nautical Charts of the Coasts of Spain and Africa) and the Derrotero de las costas de España en el Océano Atlántico y de las islas Azores o Terceras, para inteligencia y uso de las cartas esféricas (1789) (Pilot's Log-book of the Coasts of Spain in the Atlantic Ocean and of the Azores, for the use of naval intelligence and nautical charts).
Due to an error in transcription on one of Tofiño’s maps, the island of Mogro (Santander) came to be called Mouro Island. Tofino Inlet, from which the town of Tofino got its name, was named in 1792 by the Spanish explorers Galiano and Valdés, in honor of Admiral Tofiño, under whom Galiano had learned cartography.
|
Vincent Tofiño de San Miguel (Cadice 1732 - 1795 San Fernando)
|
Vicente Tofiño de San Miguel y Wanderiales (or Vanderiales) was a Spanish navigator and cosmographer. He studied experimental physics and then joined the army, which he subsequently left. In 1755 Jorge Juan asked Tofiño to join the faculty of the Academy of Marines at Cádiz (Academia de Guardia Marinas de Cádiz) as a mathematics instructor, while also allowing Tofiño to join the Armada as a second lieutenant (alférez de navío). In 1768 Tofiño was named Director of the Academy and in 1773, was named Director of the Academies of Ferrol and Cartagena as well. He participated in the expeditions against Algiers (1773) and the Great Siege of Gibraltar (1782). He acquired the rank of Brigadier of the Armada in 1784, and in 1789 the rank of Rear Admiral.
He planned the initial construction, and worked at, the Royal Institute and Observatory of the Armada (Real Instituto y Observatorio de la Armada) of the Company of Marines, publishing observations with great scientific skill, like the transit of Venus by the Sun, taking advantage of an eclipse on 3 June 1796.
Tofiño went to sea and the result of this was several works, including Derrotero de las costas de España en el mar Mediterráneo y África (1787) (Pilot's Log-book of the Coasts of Spain in the Mediterranean Sea and Africa); his colección de cartas esféricas de las costas de España y África... (1788) (Collection of Nautical Charts of the Coasts of Spain and Africa) and the Derrotero de las costas de España en el Océano Atlántico y de las islas Azores o Terceras, para inteligencia y uso de las cartas esféricas (1789) (Pilot's Log-book of the Coasts of Spain in the Atlantic Ocean and of the Azores, for the use of naval intelligence and nautical charts).
Due to an error in transcription on one of Tofiño’s maps, the island of Mogro (Santander) came to be called Mouro Island. Tofino Inlet, from which the town of Tofino got its name, was named in 1792 by the Spanish explorers Galiano and Valdés, in honor of Admiral Tofiño, under whom Galiano had learned cartography.
|