

| Reference: | S42873 |
| Author | Vincenzo CORONELLI |
| Year: | 1690 |
| Zone: | Jan Mayen |
| Printed: | Venice |
| Measures: | 314 x 235 mm |


| Reference: | S42873 |
| Author | Vincenzo CORONELLI |
| Year: | 1690 |
| Zone: | Jan Mayen |
| Printed: | Venice |
| Measures: | 314 x 235 mm |
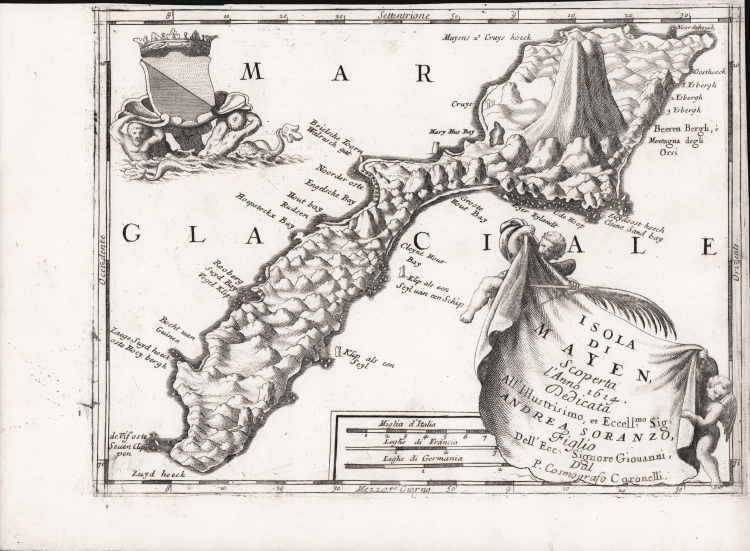
Map taken from "Corso Geografico Universale".
Scarce decorative map of Jan Mayen Island, a volcanic island in the Atlantic Ocean.
Coronelli's map of Jan Mayen celebrates its discovery in 1614.
The first known discovery of the island was in 1614. There are claims of earlier discoveries: some historians believe an Irish monk, Brendan, who was known as a good sailor, was close to Jan Mayen in the early sixth century. He came back from one of his voyages and reported he had been close to a black island, which was on fire, and there was a terrible noise in the area. He thought he might have found the entrance to hell.
Jan Mayen was discovered in the summer of 1614, probably within one month, by three separate expeditions. The Dutchman Fopp Gerritsz, while in command of a whaling expedition sent out by the Englishman John Clarke, of Dunkirk, claimed (in 1631) to have discovered the island on June 28 and named it "Isabella". In January the Noordsche Compagnie (Northern Company), modeled on the Dutch East India Company, had been established to support Dutch whaling in the Arctic. Two of its ships, financed by merchants from Amsterdam and Enkhuizen, reached Jan Mayen in July 1614. The captains of these ships-Jan Jacobszoon May van Schellinkhout on the Gouden Cath (Golden Cat) and Jacob de Gouwenaer on the Orangienboom (Orange Tree)-named it Mr. Joris Eylant after the Dutch cartographer Joris Carolus who was on board and mapped the island.
The captains acknowledged that a third Dutch ship, the Cleyn Swaentgen (Little Swan) captained by Jan Jansz Kerckhoff and financed by Noordsche Compagnie shareholders from Delft, had already been at the island when they arrived. They had assumed the latter, who named the island Maurits Eylandt (or Mauritius) after Maurice of Nassau, Prince of Orange, would report their discovery to the States General. However, the Delft merchants had decided to keep the discovery secret and returned in 1615 to hunt for their own profit. The ensuing dispute was only settled in 1617, though both companies were allowed to whale at Jan Mayen in the meantime.
Vincenzo CORONELLI (Venezia 1650 - 1718)
|
Cosmographer, geographer, biographer, encyclopedist, globe maker, inventor, expert of engeneering and hydraulics. Extraordinarily versatile mind and an extremely tireless man, he produced more than 140 pieces in different genres. At the age of 15, he entered the Franciscan Order, which he then guided as Gran Generale from 1699. He became famous as geographer and mathematician, awakening the interest in these subjects in Italy at the end of the XVII century. He travelled a lot, seeking for all that was new, and keeping a correspondance with the most important intellectuals of his time. In 1681 Louis XIV wanted him to go to France, to entrust him with the task of making two terraqueous globes (Marly Globes), with a diameter of 4 metres. Once he came back to Italy, in 1685, he became Cosmographer of the Venetian Republic, where he taught geography and founded the first geographic accademy, called The Argonauts Accademy. In his whole life he produced more that 500 maps; some of them can be found in his most famous works, such as the Venetian Atlas (1690), the Island Book of the Venetian Atlas (1696-97), the Book of Globes (1693). As far as his scientific method, he didn’t elaborate new cartographic systems, but followed the theories that were considered most popular and effective at his time, based on the Copernican system. The main characteristic of his charts is the high quantity of toponymic and historical information. In his most famous and dense work, the Venetian Atlas, we can find about 1100 plates, 200 of which are extremely technical and this is the reason why it is considered the first Italian atlas to describe and illustrate the whole world with charts and maps. It was published in 13 volumes, starting from 1690, and it took nearly ten years to finish it. It is divided in different parts, the most important are the Atlas itself, then the Island Book, the Corso Geografico and the Teatro delle città.
|
Vincenzo CORONELLI (Venezia 1650 - 1718)
|
Cosmographer, geographer, biographer, encyclopedist, globe maker, inventor, expert of engeneering and hydraulics. Extraordinarily versatile mind and an extremely tireless man, he produced more than 140 pieces in different genres. At the age of 15, he entered the Franciscan Order, which he then guided as Gran Generale from 1699. He became famous as geographer and mathematician, awakening the interest in these subjects in Italy at the end of the XVII century. He travelled a lot, seeking for all that was new, and keeping a correspondance with the most important intellectuals of his time. In 1681 Louis XIV wanted him to go to France, to entrust him with the task of making two terraqueous globes (Marly Globes), with a diameter of 4 metres. Once he came back to Italy, in 1685, he became Cosmographer of the Venetian Republic, where he taught geography and founded the first geographic accademy, called The Argonauts Accademy. In his whole life he produced more that 500 maps; some of them can be found in his most famous works, such as the Venetian Atlas (1690), the Island Book of the Venetian Atlas (1696-97), the Book of Globes (1693). As far as his scientific method, he didn’t elaborate new cartographic systems, but followed the theories that were considered most popular and effective at his time, based on the Copernican system. The main characteristic of his charts is the high quantity of toponymic and historical information. In his most famous and dense work, the Venetian Atlas, we can find about 1100 plates, 200 of which are extremely technical and this is the reason why it is considered the first Italian atlas to describe and illustrate the whole world with charts and maps. It was published in 13 volumes, starting from 1690, and it took nearly ten years to finish it. It is divided in different parts, the most important are the Atlas itself, then the Island Book, the Corso Geografico and the Teatro delle città.
|