

| Reference: | S42913 |
| Author | Giacomo CANTELLI |
| Year: | 1684 |
| Zone: | Balcani |
| Measures: | 540 x 420 mm |


| Reference: | S42913 |
| Author | Giacomo CANTELLI |
| Year: | 1684 |
| Zone: | Balcani |
| Measures: | 540 x 420 mm |
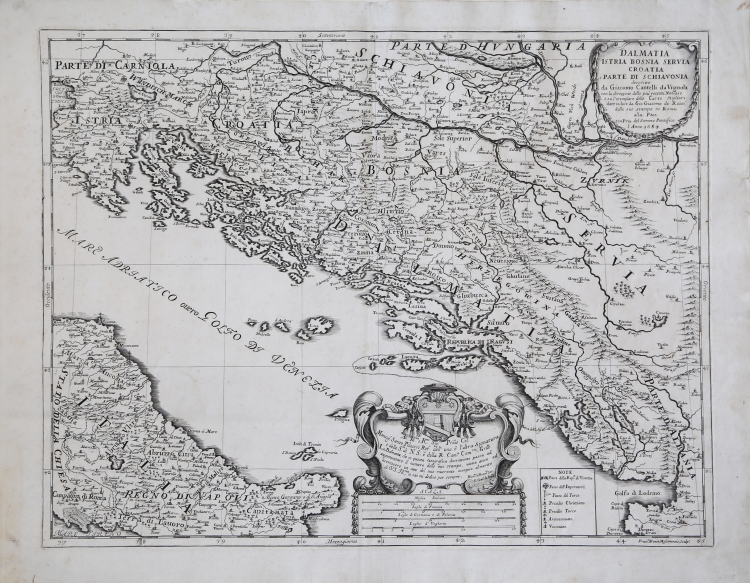
This Cantelli map shows all today's Croatian lands except the westernmost part of medieval Slavonia (today the area west of Zagreb). Croatia was supposed to be shown within its medieval borders, but they are marked by many shortcomings. Dalmatia is marked approximately within the boundaries of the former Roman province of Dalmatia. Zagreb is marked twice, once as Agram and the second time as Zagrebia. There are also many shortcomings in the presentation of the hydrographic network. The relief is represented by the method of shady moles. The map is made according to older templates, especially those of Gerhard Mercator. However, Cantelli also had some recent information, as evidenced by the distinction between Christian and Turkish-ruled settlements in Dalmatia and Herzegovina, which means that he was aware of data on Turkish conquests during the 16th and 17th centuries. The title of the map is in the upper right corner of the cartridge with plant ornaments. The scale is expressed in Italian, Polish, German and Hungarian miles.
Shows administrative divisions, cities, towns, landmarks, churches, forests, rivers and mountains.
Map taken from Mercurio geografico overo Guida Geografica in tutte le parti del Mondo conforme le Tavole Geografiche del Sansone Baudran de Cantelli Data in luce con direttione, e cura di Gio. Giacomo de Rossi nella sua stamperia collection of maps published in Rome between 1660 and 1730 by the typography De Rossi - the date of the maps goes from 1669 to 1715 - whose first edition is due to Giovanni Giacomo de Rossi. Over the years the atlas was enriched by an increasing number of maps in subsequent editions edited first by Domenico de Rossi and then by his son Filippo.
The Mercurio Geografico is a collection that brings together works by cartographers such as Michele Antonio Baudrand, Nicolas Sanson, Augustin Lubin, Filippo Titi, Giacomo Ameti, Giovanni Antonio Magini and Innocenzo Mattei, and which includes as its main "corpus" the great production of the geographer Giacomo Cantelli da Vignola. The maps are finely copied and engraved by the major engravers of the time including Falda, Widman, Barbey, Widman, Lhuillier, Donia, Mariotti.
Cantelli was a geographer and cartographer, a native of Montorsello near Vignola; duties his humanistic studies in Bologna, in 1669, he entered the service of Marquis Obizzo da Ferrara there as secretary, then went to Venice and from there to Paris, where he formed relations with the leading French geographers of the time, Du Val, Nicola Sanson and especially Michel Antoine Baudrand, with whom he then remained in constant correspondence. Returning to Bologna, he was for long years secretary to Rinieri Marescotti; but, around 1675 or shortly thereafter, he went, perhaps several times, to Rome, and entered into relations with the famous De Rossi cartographic workshop, which then published most of his maps. By this time his reputation as a cartographer had been established, so much so that he was called upon by both Pope Innocent XI and the Duke of Modena and Reggio Francesco II d'Este, both of whom wanted him as their official cartographer. He chose the court of Francesco II, and in November 1685 he was appointed court geographer. From 1686 to 1689 he executed numerous maps of European countries and territories. He constructed by his own hand a world map and a celestial globe, which remained on display for some time in the atrium of the Biblioteca Estense in Modena. He died in Modena on November 30, 1695. Almost all the maps were included in the Mercurio Geografico, the well-known atlas published in Rome by the De Rossi family. The first edition of the Mercurio Geografico published 19 of his maps, along with others by Sanson and Baudrand. A two-volume second edition came out in 1692, which contained work he had done (88 maps, engraved by Antonio Barbey).
Copperplate, some foxing, otherwise very good condition.
Literature
cfr. R. Almagià, Studi storici di cartografia napoletana, in “Archivio storico per le province napoletane”, 38 (1913), p. 645; A. Bonazzi, Il Mercurio geografico: il gioco e la differenza, in “Giacomo Cantelli: geografo del Serenissimo”, Bologna, 1995, p. 37-44 e 150-152; Bagrow 268; Phillips I 254-255; Shirley BL I, pp. 868-874.
Giacomo CANTELLI (Vignola 1643 - 1695)
|
Cantelli was a geographer and cartographer, a native of Montorsello near Vignola; duties his humanistic studies in Bologna, in 1669, he entered the service of Marquis Obizzo da Ferrara there as secretary, then went to Venice and from there to Paris, where he formed relations with the leading French geographers of the time, Du Val, Nicola Sanson and especially Michel Antoine Baudrand, with whom he then remained in constant correspondence. Returning to Bologna, he was for long years secretary to Rinieri Marescotti; but, around 1675 or shortly thereafter, he went, perhaps several times, to Rome, and entered into relations with the famous De Rossi cartographic workshop, which then published most of his maps. By this time his reputation as a cartographer had been established, so much so that he was called upon by both Pope Innocent XI and the Duke of Modena and Reggio Francesco II d'Este, both of whom wanted him as their official cartographer. He chose the court of Francesco II, and in November 1685 he was appointed court geographer. From 1686 to 1689 he executed numerous maps of European countries and territories. He constructed by his own hand a world map and a celestial globe, which remained on display for some time in the atrium of the Biblioteca Estense in Modena. He died in Modena on November 30, 1695. Almost all the maps were included in the Mercurio Geografico, the well-known atlas published in Rome by the De Rossi family. The first edition of the Mercurio Geografico published 19 of his maps, along with others by Sanson and Baudrand. A two-volume second edition came out in 1692, which contained work he had done (88 maps, engraved by Antonio Barbey).
|
Giacomo CANTELLI (Vignola 1643 - 1695)
|
Cantelli was a geographer and cartographer, a native of Montorsello near Vignola; duties his humanistic studies in Bologna, in 1669, he entered the service of Marquis Obizzo da Ferrara there as secretary, then went to Venice and from there to Paris, where he formed relations with the leading French geographers of the time, Du Val, Nicola Sanson and especially Michel Antoine Baudrand, with whom he then remained in constant correspondence. Returning to Bologna, he was for long years secretary to Rinieri Marescotti; but, around 1675 or shortly thereafter, he went, perhaps several times, to Rome, and entered into relations with the famous De Rossi cartographic workshop, which then published most of his maps. By this time his reputation as a cartographer had been established, so much so that he was called upon by both Pope Innocent XI and the Duke of Modena and Reggio Francesco II d'Este, both of whom wanted him as their official cartographer. He chose the court of Francesco II, and in November 1685 he was appointed court geographer. From 1686 to 1689 he executed numerous maps of European countries and territories. He constructed by his own hand a world map and a celestial globe, which remained on display for some time in the atrium of the Biblioteca Estense in Modena. He died in Modena on November 30, 1695. Almost all the maps were included in the Mercurio Geografico, the well-known atlas published in Rome by the De Rossi family. The first edition of the Mercurio Geografico published 19 of his maps, along with others by Sanson and Baudrand. A two-volume second edition came out in 1692, which contained work he had done (88 maps, engraved by Antonio Barbey).
|