

| Reference: | S39979 |
| Author | Laurent FRIES |
| Year: | 1522 ca. |
| Zone: | Armenia |
| Printed: | Vienne |
| Measures: | 515 x 385 mm |


| Reference: | S39979 |
| Author | Laurent FRIES |
| Year: | 1522 ca. |
| Zone: | Armenia |
| Printed: | Vienne |
| Measures: | 515 x 385 mm |
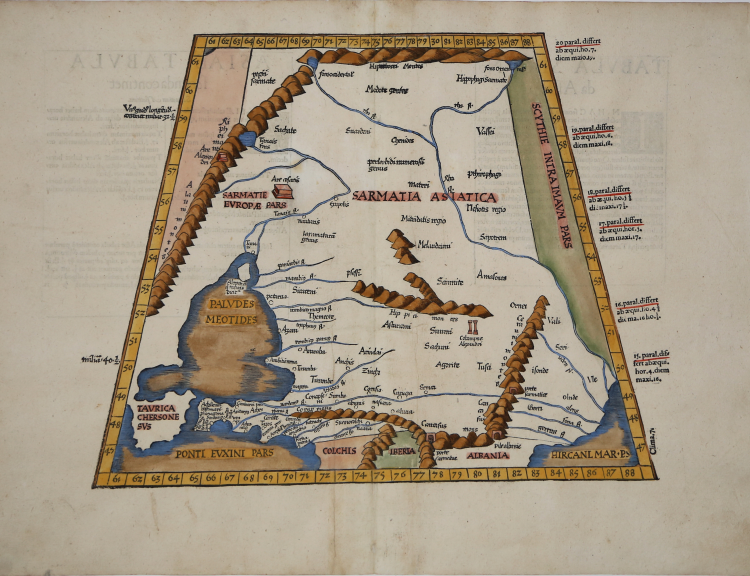
This Ptolemaic map focuses on a historical region steeped in legend, one of great importance in the early development of trade between Asia and Europe, the Silk Road region, between the Hyperborei and Caucus Mountains. It includes a portion of the Caspian Sea.
Those regions of eastern Europe which border the Black Sea are depicted, and named according to ancient kingdoms and peoples. The Black Sea has an interesting shape. Constantinople is not named, but the Bosphorus is. A number of references to the Scythians are noted. A number of other ancient civilizations are also referred to including the Sarmatians, the kingdom of Mithridatis, and the Amazons are named, but in the wrong region or Anatolia. Colchis is shown to the south of a very misshapen Anatolia. Numerous mountain ranges and river systems are shown in detail.
Nice example of the 1541 edition of Lorenz Fries map, based upon Waldseemuller's map, first published in 1513.
The first edition of Ptolemy's Geographia edited by Fries was published in Strasbourg in 1522, with maps that were copied and re-engraved from those of Martin Waldseemüller of the 1520 edition of Ptolemy and text edited by Pirckheimer. In 1525 a second edition was printed in Strasbourg. At the death of Fries and Gruninger, the plates were purchased by the brothers Melchior and Gaspar Treschel, who printed a third edition in Lyon in 1535. For the text, the two editors used the supervision of Michael Servetus, who edited Pirckheimer's text. Finally, in 1541, Gaspare Treechsel published in Vienne, in the Dauphiné, this fourth edition, again with Servetus' text. In this edition, compared to the first edition of Strasbourg in 1522, the text underwent numerous changes, corrections and additions, but the wood-blocks were not changed.
Woodcut, finely colored by hand, in excellent condition.
|
Lorenz (Laurent) Fries was born in Alsace in about 1490. He studied medicine, apparently spending time at the universities of Pavia, Piacenza, Montpellier and Vienna. After completing his medical studies, , Fries worked as a physician in several places, before settling in Strassburg, in about 1519. In Strassburg, Fries met the Strasbourg printer and publisher Johann Grüninger, an associate of the St. Die group of scholars formed by, among others, Walter Lud, Martin Ringmann and Martin Waldseemuller.From 1520 to 1525, Fries worked with Gruninger as a cartographic editor, exploiting the corpus of material that Waldseemuller had created. Fries' first venture into mapmaking was in 1520, when he executed a reduction of Martin Waldseemuller's wall-map of the World, published in 1507. Next Fries’ project was a new edition of the Geographia of Claudius Ptolemy, which was published by Johann Koberger in 1522. Fries evidently edited the maps, in most cases simply producing a reduction of the equivalent map from Waldseemuller's 1513 edition of the Geographie Opus Novissima, printed by Johann Schott. Fries also prepare three new maps for the Geographie: maps of South-East Asia and the East Indies, China and the World, but the geography of these derives from Waldseemuller's world map of 1507. The 1522 edition of Fries work , now very rare, was not commercially successful. In 1525, an improved edition was issued, from the notes of Johannes Regiomontanus. After Grüninger's death in 1531, the business was continued by his son Christoph, who seems to have sold the materials for the Ptolemy to two Lyon publishers, the brothers Melchior and Gaspar Trechsel, who published a joint edition in 1535, before Gaspar Trechsel published an edition in his own right in 1541.
|
|
Lorenz (Laurent) Fries was born in Alsace in about 1490. He studied medicine, apparently spending time at the universities of Pavia, Piacenza, Montpellier and Vienna. After completing his medical studies, , Fries worked as a physician in several places, before settling in Strassburg, in about 1519. In Strassburg, Fries met the Strasbourg printer and publisher Johann Grüninger, an associate of the St. Die group of scholars formed by, among others, Walter Lud, Martin Ringmann and Martin Waldseemuller.From 1520 to 1525, Fries worked with Gruninger as a cartographic editor, exploiting the corpus of material that Waldseemuller had created. Fries' first venture into mapmaking was in 1520, when he executed a reduction of Martin Waldseemuller's wall-map of the World, published in 1507. Next Fries’ project was a new edition of the Geographia of Claudius Ptolemy, which was published by Johann Koberger in 1522. Fries evidently edited the maps, in most cases simply producing a reduction of the equivalent map from Waldseemuller's 1513 edition of the Geographie Opus Novissima, printed by Johann Schott. Fries also prepare three new maps for the Geographie: maps of South-East Asia and the East Indies, China and the World, but the geography of these derives from Waldseemuller's world map of 1507. The 1522 edition of Fries work , now very rare, was not commercially successful. In 1525, an improved edition was issued, from the notes of Johannes Regiomontanus. After Grüninger's death in 1531, the business was continued by his son Christoph, who seems to have sold the materials for the Ptolemy to two Lyon publishers, the brothers Melchior and Gaspar Trechsel, who published a joint edition in 1535, before Gaspar Trechsel published an edition in his own right in 1541.
|