

| Reference: | S13625 |
| Author | Charles François DELAMARCHE |
| Year: | 1806 ca. |
| Zone: | The World |
| Printed: | Paris |
| Measures: | 420 x 265 mm |


| Reference: | S13625 |
| Author | Charles François DELAMARCHE |
| Year: | 1806 ca. |
| Zone: | The World |
| Printed: | Paris |
| Measures: | 420 x 265 mm |
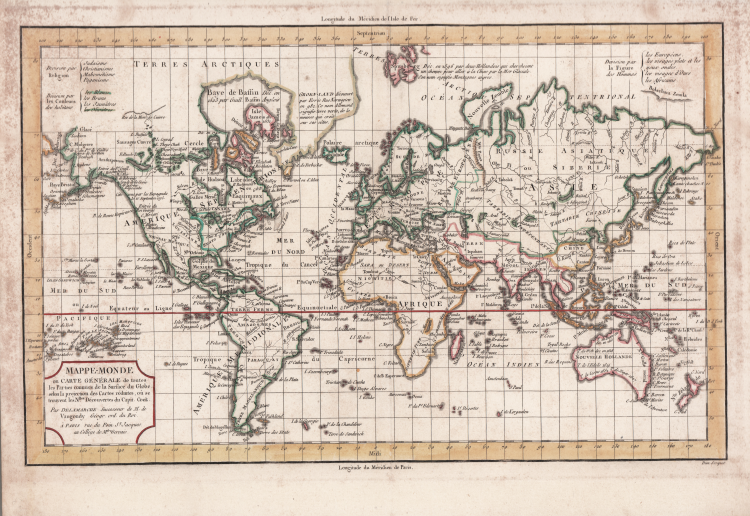
"Mappe-Monde ou Carte Generale de Toutes les Parties Connues de la Surface du Globe, Selon la Projection des Cartes Reduites, ou se Trouvent les Nlles. Decouvertes du Capit. Cook", Robert de Vaugondy/Delamarche
Copper engraved map of the world is drawn on Mercator's projection. Considering the scale, there is good detail of major place names, watershed and islands of the world. The map has been updated to illustrate the recent discoveries of Cook, La Perouse, Vancouver, and Mackenzie. Notations in the Arctic discuss recent explorations, and there is good detail of the islands of the Pacific. This map was issued in three versions based on the three legends at top, depicting how the world is divided by religion, skin color, and facial features. Title cartouche notes that Delamarche is the successor to Robert de Vaugondy.
Plate taken from the Recueil de cartes sur la géographie ancienne et moderne, à l'usage des élèves de l'Ecole Royale Militaire de Saint-Cyr, printed in Paris and published in several editions between 1806 and 1825.
Charles-François Delamarche (August 1740 – 31 October 1817) was a French geographer and mapmaker. One of the most important French geographers and mapmakers of the second half of the eighteenth century. Successor to Nicolas Sanson (1600 – 1667), Robert de Vaugondy (1686 – 1766), and Rigobert Bonne (1727 – 1794), whose atlases he reprinted. Also taught geography. In addition to maps and globes, his works include a treatise on the use of the sphere and celestial and terrestrial globes. In the treatise, he illustrates both the Ptolemaic and Copernican systems, as well as listing all the ancient and modern constellations. His son Félix Delamarche continued his work. Charles François Delamarche acquired Didier Robert de Vaugondy's collection in 1778, after having collaborated with him in the edition of atlases.
Etching, printed on contemporary laid paper, a fine later hand coloring, some foxing, otherwise excellent condition.
Bibliografia
Moreland-Bannister “Antique Maps A Collector’s Guide” Oxford 1989 pag.136 e 139.
Charles François DELAMARCHE (1740 – 1817)
|
One of the most important French geographers and mapmakers of the second half of the eighteenth century. Successor to Nicolas Sanson (1600 – 1667), Robert de Vaugondy (1686 – 1766), and Rigobert Bonne (1727 – 1794), whose atlases he reprinted. Also taught geography. In addition to maps and globes, his works include a treatise on the use of the sphere and celestial and terrestrial globes. In the treatise, he illustrates both the Ptolemaic and Copernican systems, as well as listing all the ancient and modern constellations.
|
Charles François DELAMARCHE (1740 – 1817)
|
One of the most important French geographers and mapmakers of the second half of the eighteenth century. Successor to Nicolas Sanson (1600 – 1667), Robert de Vaugondy (1686 – 1766), and Rigobert Bonne (1727 – 1794), whose atlases he reprinted. Also taught geography. In addition to maps and globes, his works include a treatise on the use of the sphere and celestial and terrestrial globes. In the treatise, he illustrates both the Ptolemaic and Copernican systems, as well as listing all the ancient and modern constellations.
|