- New


| Reference: | S48760 |
| Author | Giuseppe REMONDINI |
| Year: | 1804 |
| Zone: | The World |
| Printed: | Venice |
| Measures: | 660 x 485 mm |



| Reference: | S48760 |
| Author | Giuseppe REMONDINI |
| Year: | 1804 |
| Zone: | The World |
| Printed: | Venice |
| Measures: | 660 x 485 mm |
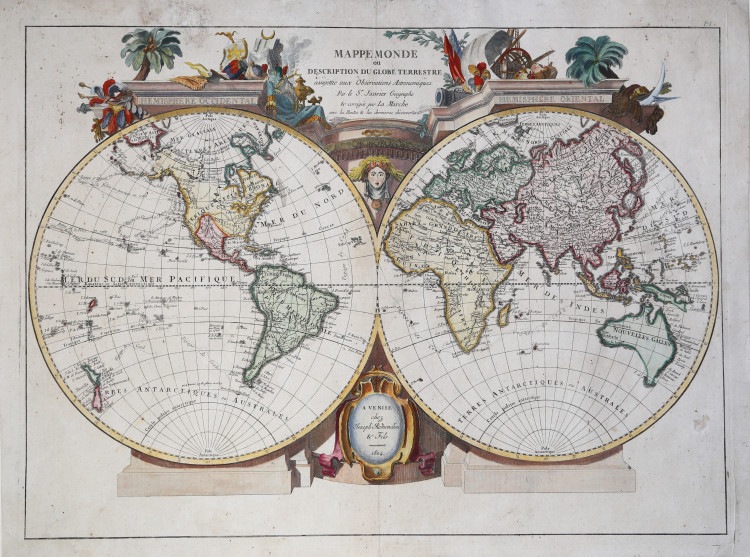
Rare separately published and significantly updated map of the world by Giuseppe Remondini featuring the voyages of Captain James Cook and other explorers of the late 18th century.
Mappe Monde ou Description Du Globe Terrestre assujettie aux Observations Astronomiques Par le SR. Janvier & corrigee par Lar Marche avec les Routes & les dernieres decouvertes . . . 1804
Extraordinary large-format double hemisphere decorative map of the world, published in Venice in 1804. First printed by Francesco Santini for his of the Atlas Universel in 1776 and reprinted, unaltered, by Giuseppe Remondini in 1784, the world map is based on the geography of Robert Jean Janvier (active 1746-76) a French cartographer of the second half of the 18th century about whom little information is available.
This rare copy - separately published and not belonging to an atlas - which we can describe as a third state or plate edition, has been significantly updated to include the progress of the voyages of Captain James Cook and other late 18th century explorers.
Details about the Antarctic region have been completely removed, while details of explorations along the northwest coast of America and in search of the Northwest Passage have been included, up to the information reported by Arrowsmith in the late 18th century. The most notable information and new features come from the South Seas; now Oceania is “correctly” delineated with the west coasts and named Nouvelles Galles; New Zealand is fully represented, and the Sandwich Isles (Hawaii) appear, not found in previous editions of the map. All this new information is derived by Francois Delamarche as stated in the title of the map “corrigée par La Marche avec ler Routes & les derniers découvertes”.
This edition of the map is extremely rare; it is the second copy of which we are aware.
The Remondinis were a family of printers who operated in Bassano del Grappa from the mid-17th to mid-19th centuries, founded by Giovanni Antonio Remondini (Padua in 1634 - Bassano 1711), around 1657, who was succeeded by his son Giuseppe (Bassano 1672 - ivi circa 1750) and his descendants. Giuseppe gave a decisive development to the enterprise, taking ownership, or at least control, of several paper factories. An extraordinary variety of products began to emerge from the Bassano workshops, whose iconographic imagery depended heavily on fashions and their evolutions: fans, board games of all kinds made even in different languages, playing cards, optical views of cities used in new world shows, prints prepared to be glued to furniture called "a lacca povera" or on other objects, such as boxes and snuff boxes, sheets with figures to be cut out with groups of images such as nativity scenes, toy soldiers, crafts, business cards, wallpaper, all materials punctually recorded in the very rich catalogs that from 1729 began to be regularly published and that constitute one of the main sources for the study of the Remondini's production. Giuseppe also oversaw the establishment of a workshop entrusted to the care of Giuliano Giampiccoli and then Antonio Baratti for the practical training of the engravers needed by the firm, improperly referred to as a "school of intaglio." He also implanted a printing house in Venice, and here his son Giovan Battista (Bassano 1713 - Castello Tesino 1776) called the best engravers of the time to collaborate. With Giovan Battista's son Giuseppe (Bassano 1754 - ivi 1811) and his brother Antonio Bartolomeo, intaglio printing reached an important dimension; production increased to a planetary level.
Etching, contemporary coloring with retouching, in very good condition.
Bibliografia
A. Bertarelli, La Remondiniana di Bassano Veneto, in “Emporium”, LXVIII (1928), pp. 358-369; M. Infelise, I Remondini di Bassano. Stampa e industria nel Veneto del Settecento, Bassano del Grappa 1990; A.W.A. Boschloo, The prints of the Remondinis: an attempt to reconstruct an eighteenth-century world of pictures, Amsterdam 1998; L. Carnelos, I libri da risma. Catalogo delle edizioni R. a larga diffusione (1650-1850), Milano 2008; A. Milano, Selling prints for the R.’: Italian pedlars from the Tesino and Natisone Valleys travelling through Europe during the eighteenth century, in Not dead things the dissemination of popular print in England and Wales, Italy, and the Low Countries, 1500-1820, Amsterdam 2013, pp 75-96.
Giuseppe REMONDINI (1745 - 1811)
|
The Remondinis were a family of printers who operated in Bassano del Grappa from the mid-17th to mid-19th centuries. Giovanni Antonio Remondini was born in Padua in 1634. In 1657, in his early twenties, he took up residence in Bassano's main square. He opened a store selling cloth, wools, silks and iron tools. Later, he added woodcuts of saints and popular subjects, which peasants bought to protect their homes, to his wares. Remondini developed his own print shop, purchasing an old press, from which originated one of the most important intaglio prints in Europe. To the brightly colored prints were added games, such as the goose ride or paper soldiers, and story booklets to satisfy the tastes of the petty people. In 1711, upon the founder's death, the estate was divided among the heirs, and the printing house fell to his son Giuseppe (Bassano 1672 - circa 1750), and his descendants. Giuseppe imprinted a marked development on the enterprise, taking ownership, or at least control, of several paper mills.
An extraordinary variety of products began to emerge from the Bassano workshops, whose iconographic imagery depended heavily on fashions and their evolutions: fans, board games of all kinds made even in different languages, playing cards, optical views of cities used in new world shows, prints prepared to be glued to furniture called "a lacca povera" or on other objects, such as boxes and snuff boxes, sheets with figures to be cut out with groups of images such as nativity scenes, toy soldiers, crafts, business cards, wallpaper, all materials punctually recorded in the very rich catalogs that from 1729 began to be regularly published and that constitute one of the main sources for the study of the Remondini's production (Remondini, 1990, pp. 77-81; Carnelos, 2008, pp. 37-39). Giuseppe also oversaw the establishment of a workshop entrusted to the care of Giuliano Giampiccoli and then Antonio Baratti for the practical training of the engravers needed by the firm, improperly referred to as a "school of intaglio." He also implanted a printing house in Venice, and here his son Giovan Battista (Bassano 1713 - Castello Tesino 1776) called the best engravers of the time to collaborate. With Giovan Battista's son Giuseppe (Bassano 1754 - ivi 1811) and his brother Antonio Bartolomeo, the intaglio reached an important dimension; production increased to a planetary level. The old network of door-to-door salesmen was replaced by an efficient network of distributors on their own, organized by geographical areas. The Tesini covered Europe from Germany to the Nordic countries, then pushed westward to the Americas; the Schiavoni, entrusted with the entire east of the world, reached as far as the Pacific Ocean. With these two major distribution centers, the printing house's commercial network was able to reach four continents.
Under the direction of Giuseppe's son Francesco Girolamo (1773-1820) it was, however, shaken by legal disputes and political events; the decline began in the first half of the 19th century, after the Napoleonic invasions. At the turn of the century the Remondini printing works had 18 presses for letterpress and woodcut impressions, 24 for copperplate engravings, equipment for printing special papers and wallpapers, 4 paper mills and a foundry for lead typefaces, employing more than 1,000 workers. By 1840 production was still substantial, but unsold goods were already piling up. In 1848 the collapse began; the stores were closed, and all the material sold (1859-60), and in 1861 the company closed its doors.
Bibliografia
A. Bertarelli, La Remondiniana di Bassano Veneto, in “Emporium”, LXVIII (1928), pp. 358-369; M. Infelise, I Remondini di Bassano. Stampa e industria nel Veneto del Settecento, Bassano del Grappa 1990; A.W.A. Boschloo, The prints of the Remondinis: an attempt to reconstruct an eighteenth-century world of pictures, Amsterdam 1998; L. Carnelos, I libri da risma. Catalogo delle edizioni R. a larga diffusione (1650-1850), Milano 2008; A. Milano, Selling prints for the R.’: Italian pedlars from the Tesino and Natisone Valleys travelling through Europe during the eighteenth century, in Not dead things the dissemination of popular print in England and Wales, Italy, and the Low Countries, 1500-1820, Amsterdam 2013, pp 75-96.
|
Giuseppe REMONDINI (1745 - 1811)
|
The Remondinis were a family of printers who operated in Bassano del Grappa from the mid-17th to mid-19th centuries. Giovanni Antonio Remondini was born in Padua in 1634. In 1657, in his early twenties, he took up residence in Bassano's main square. He opened a store selling cloth, wools, silks and iron tools. Later, he added woodcuts of saints and popular subjects, which peasants bought to protect their homes, to his wares. Remondini developed his own print shop, purchasing an old press, from which originated one of the most important intaglio prints in Europe. To the brightly colored prints were added games, such as the goose ride or paper soldiers, and story booklets to satisfy the tastes of the petty people. In 1711, upon the founder's death, the estate was divided among the heirs, and the printing house fell to his son Giuseppe (Bassano 1672 - circa 1750), and his descendants. Giuseppe imprinted a marked development on the enterprise, taking ownership, or at least control, of several paper mills.
An extraordinary variety of products began to emerge from the Bassano workshops, whose iconographic imagery depended heavily on fashions and their evolutions: fans, board games of all kinds made even in different languages, playing cards, optical views of cities used in new world shows, prints prepared to be glued to furniture called "a lacca povera" or on other objects, such as boxes and snuff boxes, sheets with figures to be cut out with groups of images such as nativity scenes, toy soldiers, crafts, business cards, wallpaper, all materials punctually recorded in the very rich catalogs that from 1729 began to be regularly published and that constitute one of the main sources for the study of the Remondini's production (Remondini, 1990, pp. 77-81; Carnelos, 2008, pp. 37-39). Giuseppe also oversaw the establishment of a workshop entrusted to the care of Giuliano Giampiccoli and then Antonio Baratti for the practical training of the engravers needed by the firm, improperly referred to as a "school of intaglio." He also implanted a printing house in Venice, and here his son Giovan Battista (Bassano 1713 - Castello Tesino 1776) called the best engravers of the time to collaborate. With Giovan Battista's son Giuseppe (Bassano 1754 - ivi 1811) and his brother Antonio Bartolomeo, the intaglio reached an important dimension; production increased to a planetary level. The old network of door-to-door salesmen was replaced by an efficient network of distributors on their own, organized by geographical areas. The Tesini covered Europe from Germany to the Nordic countries, then pushed westward to the Americas; the Schiavoni, entrusted with the entire east of the world, reached as far as the Pacific Ocean. With these two major distribution centers, the printing house's commercial network was able to reach four continents.
Under the direction of Giuseppe's son Francesco Girolamo (1773-1820) it was, however, shaken by legal disputes and political events; the decline began in the first half of the 19th century, after the Napoleonic invasions. At the turn of the century the Remondini printing works had 18 presses for letterpress and woodcut impressions, 24 for copperplate engravings, equipment for printing special papers and wallpapers, 4 paper mills and a foundry for lead typefaces, employing more than 1,000 workers. By 1840 production was still substantial, but unsold goods were already piling up. In 1848 the collapse began; the stores were closed, and all the material sold (1859-60), and in 1861 the company closed its doors.
Bibliografia
A. Bertarelli, La Remondiniana di Bassano Veneto, in “Emporium”, LXVIII (1928), pp. 358-369; M. Infelise, I Remondini di Bassano. Stampa e industria nel Veneto del Settecento, Bassano del Grappa 1990; A.W.A. Boschloo, The prints of the Remondinis: an attempt to reconstruct an eighteenth-century world of pictures, Amsterdam 1998; L. Carnelos, I libri da risma. Catalogo delle edizioni R. a larga diffusione (1650-1850), Milano 2008; A. Milano, Selling prints for the R.’: Italian pedlars from the Tesino and Natisone Valleys travelling through Europe during the eighteenth century, in Not dead things the dissemination of popular print in England and Wales, Italy, and the Low Countries, 1500-1820, Amsterdam 2013, pp 75-96.
|